I. Introduction
A Brief overview of gas CFD trading
Gas CFD (Contract for Difference) trading involves speculating on the price movements of gas contracts without owning the actual underlying asset. It is a derivative financial instrument that allows traders to profit from the difference between the opening and closing prices of gas contracts. Gas CFD trading provides flexibility and liquidity to market participants, allowing them to enter and exit positions quickly.
Gas CFD trading typically takes place on online trading platforms provided by brokers like VSTAR. Traders can access real-time price quotes, execute trades, and manage their positions through these platforms. The price of gas CFDs is usually based on futures contracts for natural gas or other gas-related commodities. The trader's goal is to predict whether the price will rise or fall and take a corresponding long or short position.
Importance of understanding the risks involved

Source: agcs.allianz.com
Understanding the risks involved in gas CFD trading is crucial for any trader. First and foremost, there is the risk of price volatility. Gas prices can be influenced by various factors, including supply and demand dynamics, geopolitical events, weather conditions, and regulatory changes. These factors can lead to significant price fluctuations, which can result in substantial profits or losses for CFD traders.
Leverage is another important aspect to consider. CFDs allow traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment, as they only need to deposit a fraction of the total trade value as margin. While leverage can amplify potential profits, it also amplifies losses. If the market moves against a trader's position, they may be required to deposit additional funds to maintain the trade, known as a margin call.
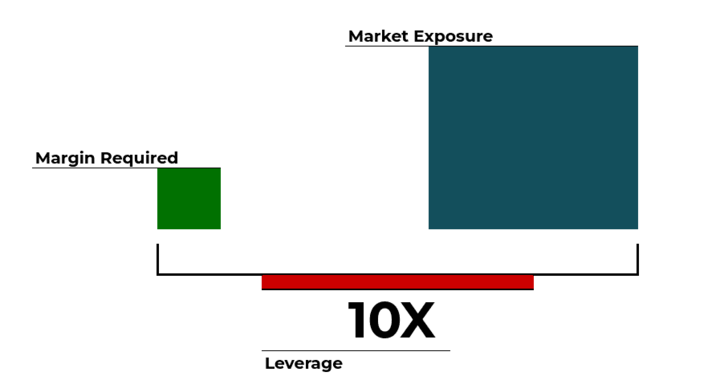
Additionally, gas CFD trading involves counterparty risk. Traders enter into contracts with brokers, and if the broker becomes insolvent or fails to fulfill their obligations, the trader may suffer financial losses. It is essential to choose a reputable and regulated broker to mitigate this risk.
Lastly, traders should consider the impact of transaction costs, such as spreads and commissions, which can reduce profitability.
II. Market Risks
Gas CFD trading exposes traders to various market risks that can significantly impact their positions and profitability. Understanding these risks is essential for traders to make informed decisions and implement effective risk management strategies.

Volatility and price fluctuations
Gas prices can be highly volatile, influenced by a range of factors such as weather conditions, economic indicators, and geopolitical events. Volatility can lead to rapid price fluctuations, creating both opportunities and risks for traders. Sudden price movements can result in significant profits or losses, depending on the direction of the trade.
To mitigate this risk, diversification is key. Traders can spread their risk by trading multiple gas contracts or diversifying their portfolio across different commodities. Diversification helps reduce the impact of a single price movement and can provide a more balanced risk-return profile.
Furthermore, risk management tools such as stop-loss orders and take-profit orders can be utilized. A stop-loss order sets a predetermined price level at which a losing position will be automatically closed, limiting potential losses. Take-profit orders, on the other hand, specify a price level at which a profitable trade will be automatically closed, securing gains. By implementing these tools, traders can manage their risk exposure and protect themselves from extreme price movements.
Supply and demand factors
Gas prices are heavily influenced by supply and demand dynamics. Factors such as production levels, storage capacities, and seasonal demand fluctuations can impact gas prices. Unexpected changes in supply or demand can lead to significant price swings.
To understand and mitigate the risks associated with supply and demand factors, traders should stay informed about industry news, market reports, and government policies that affect the gas market. By keeping up with relevant information, traders can anticipate potential shifts in supply or demand and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
Geopolitical risks
Geopolitical events can have a significant impact on gas prices. Political tensions, conflicts, and regulatory changes in major gas-producing or consuming regions can disrupt supply chains and affect prices. For example, political instability in a gas-producing country may lead to supply disruptions, causing prices to rise.
To manage geopolitical risks, traders should stay informed about global events that can impact gas markets. News sources, economic reports, and geopolitical analyses can provide valuable insights into potential risks and opportunities. Additionally, setting price alerts for specific gas contracts can help traders stay updated on significant price movements triggered by geopolitical events.
Mitigation strategies:
In addition to diversification and staying informed, traders can utilize various tools and techniques to mitigate market risks in gas CFD trading.
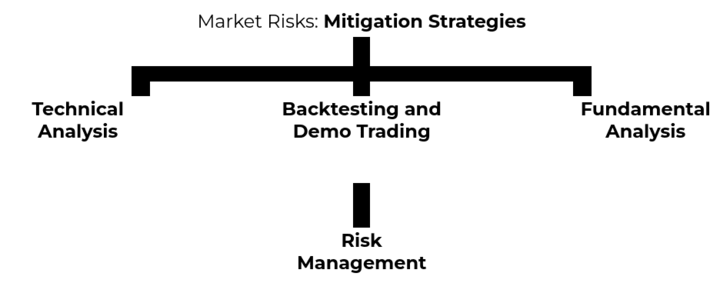
● Technical Analysis: Technical analysis involves studying historical price data, charts, and indicators to identify patterns and trends. Traders can use technical analysis to make informed decisions about when to enter or exit positions. By analyzing price patterns, support and resistance levels, and various technical indicators, traders can gain insights into potential price movements and adjust their trading strategies accordingly.
● Risk Management: Implementing effective risk management techniques is crucial in gas CFD trading. Traders should determine their risk tolerance and set appropriate position sizes and leverage levels. It is important to avoid overleveraging, as it can amplify losses in the event of adverse market moves. Additionally, using stop-loss orders and take-profit orders helps manage risk by defining exit points and limiting potential losses.
● Backtesting and Demo Trading: Before committing real funds, traders can backtest their trading strategies using historical price data. Backtesting allows traders to assess the performance of their strategies under different market conditions. Additionally, demo trading platforms provided by brokers enable traders to practice trading in a simulated environment without risking real money. These tools can help traders gain experience, refine their strategies, and identify potential weaknesses.
● Fundamental Analysis: Fundamental analysis involves analyzing economic, financial, and geopolitical factors that can impact gas prices. Traders can assess supply and demand fundamentals, industry reports, economic indicators, and political developments to make informed trading decisions. Fundamental analysis complements technical analysis and can provide a deeper understanding of the underlying drivers of gas prices.
III. Trading Risks
Gas CFD trading involves several trading risks that traders should be aware of and effectively manage to protect their capital and achieve their trading goals.
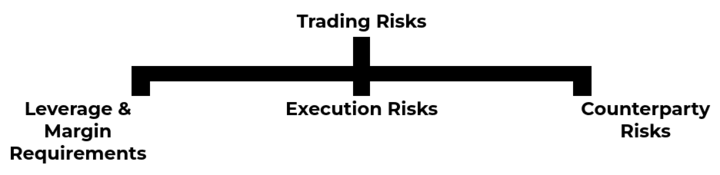
Leverage and margin requirements
One of the significant advantages of CFD trading is the ability to use leverage, which allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller initial investment. However, leverage amplifies both potential profits and losses. While it offers the opportunity for higher returns, it also increases the risk of exposure.
Traders must understand the concept of margin requirements, which is the amount of money required as collateral to open and maintain a leveraged position. If the market moves against a trader's position, they may be required to deposit additional funds to meet margin calls. Failure to do so can result in the automatic closure of their position, potentially incurring substantial losses.
To mitigate the risk associated with leverage and margin requirements, traders should carefully consider their risk tolerance and set appropriate position sizes and leverage levels. It is crucial to avoid over-leveraging, as excessive leverage can amplify losses and put traders at a higher risk of margin calls. Additionally, utilizing risk management tools such as stop-loss orders can help limit potential losses and protect capital.
Execution risks
Execution risks refer to the potential issues that can arise during the process of entering or exiting a trade. These risks can include slippage, where the execution price differs from the expected price, and latency, which is the delay between placing a trade and its execution.
Slippage can occur during periods of high market volatility or low liquidity, resulting in a less favorable entry or exit price. Latency can be caused by technical issues, slow internet connections, or delays in order processing. These risks can impact the profitability of trades and hinder the achievement of desired price levels.
To minimize execution risks, traders should choose a reputable broker with a reliable trading platform and strong execution capabilities. It is also important to monitor trades closely and be aware of market conditions that may increase the likelihood of slippage or latency. By staying informed and using brokers with efficient trade execution, traders can reduce the impact of execution risks.
Counterparty risks
Counterparty risk is the risk that the broker or counterparty with whom the trader enters into a CFD contract fails to meet its obligations. If the counterparty becomes insolvent or defaults, the trader may face challenges in accessing funds, closing positions, or recovering their capital.
To mitigate counterparty risks, it is crucial to choose a reputable and regulated broker. Regulatory oversight provides some level of protection for traders' funds and ensures that brokers adhere to certain standards and operational requirements. Traders should conduct thorough research, review customer reviews and ratings, and select a broker with a strong reputation and a track record of financial stability.
Additionally, traders can consider using risk management tools provided by brokers, such as negative balance protection. This feature ensures that traders' account balances cannot fall below zero, preventing them from owing money to the broker in the event of significant losses.
Mitigation strategies
To effectively mitigate trading risks in gas CFD trading, traders can employ several strategies:
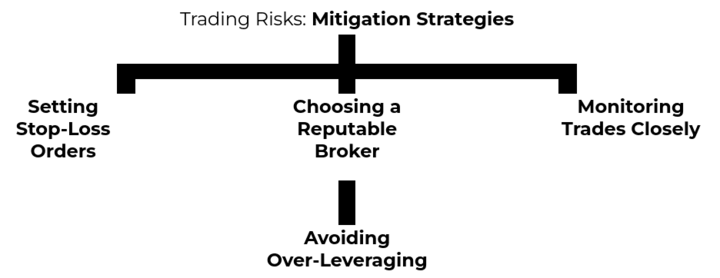
● Setting Stop-Loss Orders: Placing stop-loss orders allows traders to specify a price level at which a losing position will be automatically closed. This helps limit potential losses and provides a predefined exit point if the market moves against the trader's position.
● Choosing a Reputable Broker: Selecting a reliable and regulated broker is vital to mitigating counterparty risks. Traders should research brokers thoroughly and consider their reputation, financial stability, and regulatory compliance. It is also important to review the broker's terms and conditions, including risk management policies and client fund protection measures.
● Monitoring Trades Closely: Regularly monitoring open positions is essential to responding quickly to market developments and potential risks. Traders should stay informed about relevant news, economic indicators, and events that can impact gas prices. By actively managing trades and making informed decisions, traders can adjust their positions or implement risk management measures as necessary.
● Using Risk Management Tools: Brokers often provide risk management tools such as guaranteed stop-loss orders, take-profit orders, and trailing stops. These tools can help traders manage their risk exposure, protect profits, and limit potential losses. Understanding and utilizing these risk management features can enhance the overall risk management strategy.
● Avoiding Over-Leveraging: Carefully managing leverage is crucial to mitigating trading risks. Traders should evaluate their risk tolerance, set appropriate leverage levels, and avoid excessive leverage that can lead to larger losses and margin calls. It is important to maintain a balance between potential returns and risk exposure.
IV. Regulatory Risks
Regulatory risks play a critical role in gas CFD trading, as changes in regulations and compliance requirements can have a significant impact on the trading environment. It is crucial for traders to understand and navigate these risks to ensure compliance, protect their investments, and maintain a secure trading environment.
Changes in regulations and policies
Regulations and policies governing the gas market can change over time due to factors such as government interventions, legislative amendments, or international agreements. These changes can introduce new rules, restrictions, or reporting requirements that can affect gas CFD trading.
Traders must stay up-to-date with regulatory changes that may impact their trading activities. This can be achieved by monitoring official announcements, regulatory websites, and industry news sources. Staying informed helps traders understand and adapt to new regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance and minimizing the risk of penalties or legal consequences.
Compliance risks
Compliance risks arise from the failure to adhere to applicable laws, regulations, and industry best practices. Gas CFD traders must comply with various regulatory obligations, including anti-money laundering (AML) and know-your-customer (KYC) requirements, reporting obligations, and risk disclosure requirements. Failure to comply with these obligations can result in legal and financial consequences.
To mitigate compliance risks, traders should choose a regulated broker that operates in compliance with relevant regulatory frameworks. Regulated brokers are subject to oversight and must adhere to strict compliance standards, providing an added layer of protection for traders. Traders should thoroughly review the broker's compliance policies, terms and conditions, and privacy policy to ensure their activities align with regulatory requirements.
Moreover, traders should follow best practices and guidelines provided by regulatory authorities. This includes properly verifying their identity, maintaining accurate records, reporting suspicious transactions, and complying with tax obligations. By actively managing compliance risks, traders can protect themselves from legal issues and maintain the integrity of their trading activities.
Mitigation strategies
To effectively manage regulatory risks in gas CFD trading, traders can employ the following strategies:
● Staying Up-to-Date with Regulatory Changes: Traders should proactively monitor regulatory developments, including changes in laws, regulations, and policies that impact gas CFD trading. Subscribing to regulatory updates, following relevant news sources, and engaging with industry forums can help traders stay informed about regulatory changes. This knowledge enables them to adjust their trading strategies and ensure compliance with new requirements.
● Choosing a Regulated Broker: Opting for a regulated broker is crucial to mitigating regulatory risks. Regulated brokers are subject to oversight by regulatory authorities, ensuring they comply with legal and operational standards. Traders should verify the regulatory status of a broker before opening an account, confirming that the broker is licensed and authorized to provide financial services.
● Following Best Practices: Adhering to industry best practices and guidelines is essential for maintaining compliance and minimizing regulatory risks. Traders should follow recommended procedures for client identification, risk management, data protection, and reporting obligations. By incorporating best practices into their trading activities, traders can reduce the likelihood of compliance issues.
● Seeking Legal Advice if Necessary: In cases of complex regulatory requirements or uncertainty, traders may consider seeking legal advice from professionals experienced in financial regulations. Legal experts can provide guidance on compliance obligations, help interpret regulatory changes, and address any legal concerns. Seeking legal advice can provide clarity and mitigate potential regulatory risks.
V. Operational Risks
Operational risks are an inherent part of any trading activity, including the use of trading platforms. These risks primarily stem from technical issues, system failures, and cybersecurity vulnerabilities. Traders must be aware of these risks and implement effective mitigation strategies to ensure a smooth and secure trading experience.
Technical issues and system failures
Trading platforms heavily rely on complex technical infrastructure, including servers, networks, and software. However, technical issues and system failures can occur, leading to disruptions in trading activities. These issues may result from hardware or software malfunctions, connectivity problems, or infrastructure failures.
To mitigate the risk of technical issues and system failures, traders should choose a reliable trading platform, such as VSTAR, which emphasizes operational stability and uptime. By selecting a platform with a robust technical infrastructure, traders can minimize the likelihood of disruptions and ensure consistent access to the markets.
Additionally, traders can implement their own measures to mitigate technical risks. These measures may include regularly updating their software and antivirus programs, using stable internet connections, and employing backup systems or alternative trading platforms as contingency plans. Being prepared for technical issues can help traders mitigate the potential impact on their trading activities.
Cybersecurity risks
Cybersecurity risks pose a significant concern in online trading, as trading platforms store sensitive personal and financial information. Cybercriminals may attempt to gain unauthorized access to trading accounts, steal personal data, or manipulate trading activities for their own gain.
To mitigate cybersecurity risks, traders should choose a trading platform that prioritizes security measures. VSTAR, for example, emphasizes its commitment to cybersecurity and may employ advanced security protocols, encryption methods, and secure data storage practices.
Traders can also take proactive steps to enhance their own cybersecurity. Using strong, unique passwords and implementing two-factor authentication can add an extra layer of security to trading accounts. Regularly monitoring account activity and promptly reporting any suspicious or unauthorized access can also help detect and address cybersecurity threats.
Furthermore, maintaining up-to-date antivirus software, regularly patching and updating operating systems and applications, and avoiding clicking on suspicious links or downloading unknown files are essential practices to mitigate cybersecurity risks.
Mitigation strategies
To effectively manage operational risks in trading, traders can implement the following mitigation strategies:
● Choosing a Reliable Trading Platform: Selecting a reputable and regulated trading platform like VSTAR can significantly reduce operational risks. Trusted platforms prioritize stability, security, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Traders should conduct thorough research, read reviews, and consider the platform's track record before opening an account.
● Implementing Security Measures: Traders should take proactive steps to enhance the security of their trading activities. This includes using strong, unique passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly updating security software and applications. Additionally, maintaining awareness of common cybersecurity threats and practicing safe browsing habits can help mitigate risks.
● Having a Backup Plan: Traders should have contingency plans in place to address potential technical issues or system failures. This may involve having access to alternative trading platforms or backup systems to ensure uninterrupted trading. Being prepared for contingencies can minimize disruptions and protect trading positions.
● Regularly Updating Software and Antivirus Programs: Keeping software and antivirus programs up-to-date is crucial to address potential vulnerabilities and protect against emerging threats. Traders should regularly install updates and patches provided by software vendors to ensure the latest security enhancements are in place.
VI. Conclusion
A Recap of the risks involved in gas CFD trading
Gas CFD trading exposes traders to market risks, including volatility and price fluctuations, as well as supply and demand factors. These risks can result in potential losses if not carefully managed. Additionally, trading risks such as leverage and margin requirements, execution risks, and counterparty risks pose further challenges. Traders must also consider regulatory risks, including changes in regulations and compliance obligations that can impact trading activities.
The Importance of mitigating risks to protect investments
Mitigating risks is crucial to protecting investments and enhancing the chances of success in gas CFD trading. Traders should implement various strategies to manage risks effectively. Diversification can help reduce exposure to a single asset or market and spread the risk across different instruments. Risk management tools such as stop-loss orders, take-profit orders, and trailing stops can be employed to limit potential losses and protect profits.
Staying informed is another important aspect of risk mitigation. Traders should continuously educate themselves about the gas market, industry trends, and economic indicators that impact prices. By staying informed, traders can make informed trading decisions and adjust their positions based on market developments.
Choosing a reputable broker (like VSTAR) is crucial to mitigating trading and operational risks. A regulated broker provides an added layer of security and ensures compliance with regulatory standards. Traders should thoroughly research and select a broker that meets their specific needs and offers reliable trading conditions, such as competitive fees and deep liquidity.
Regularly monitoring trades and maintaining a disciplined approach are key risk management practices. Traders should closely monitor their positions, implement risk management measures, and avoid over-leveraging. By managing risk on an ongoing basis, traders can respond promptly to market changes and protect their capital.
Final thoughts and recommendations
Seeking professional advice is recommended, especially for novice traders or those facing complex trading scenarios. Professional advisors or financial experts can provide valuable insights, help navigate regulatory requirements, and offer guidance on risk management strategies.
Continuously educating oneself is vital in the ever-evolving world of gas CFD trading. Traders should invest time in learning about trading strategies, technical analysis, and risk management techniques. By expanding their knowledge and skills, traders can improve their decision-making abilities and adapt to changing market conditions.




