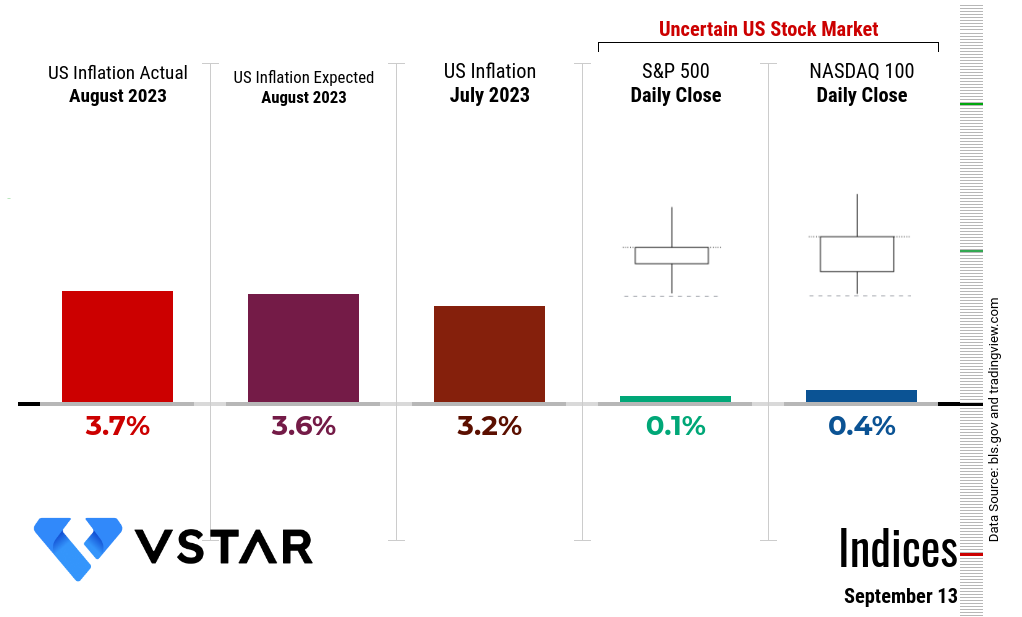
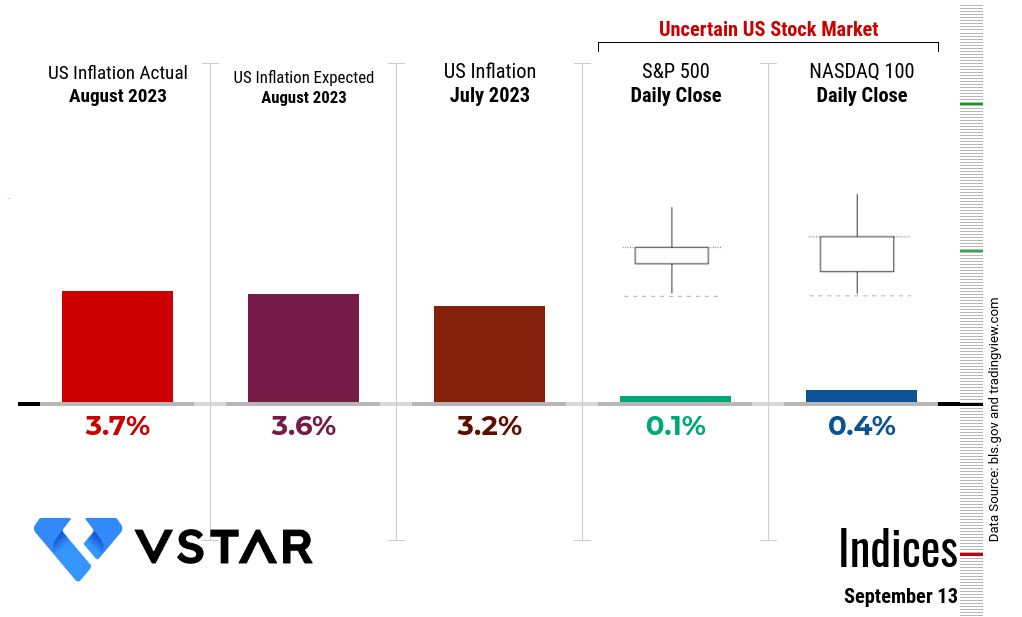
US Inflation August 2023
The August 2023 Consumer Price Index (CPI) report reveals several key trends and vital numerical values.
Firstly, the overall CPI-U increased by 0.6 percent in August, following a 0.2 percent increase in July. This indicates a higher rate of inflation and raises concerns about rising prices, which can impact consumers' purchasing power and overall economic stability.
Over the past 12 months, the all-items index increased by 3.7 percent, indicating a persistent upward trend in inflation. This figure surpasses the 3.2 percent increase reported in July, highlighting the acceleration of inflationary pressures.
The energy index experienced a notable increase of 5.6 percent in August, driven primarily by a substantial 10.6 percent rise in the gasoline index. This surge in energy costs could have cascading effects on various sectors of the economy, such as transportation and manufacturing, potentially leading to higher production costs and consumer prices.
The food index also showed a 0.2 percent increase in August, similar to the previous month. However, there were variations among food categories. While some segments, like meats, poultry, fish, and eggs experienced significant price hikes, others like dairy and related products, saw declines. Monitoring these fluctuations is crucial for assessing food price stability and its impact on household budgets.
The index for all items less food and energy, a key indicator of core inflation, rose by 0.3 percent in August. This follows a 0.2 percent increase in July, suggesting a persistent upward trend in core inflation. Of particular note is the shelter index, which increased by 0.3 percent and was a significant contributor to the core index's rise. Housing costs play a pivotal role in consumers' overall expenses, and any sustained increase could affect their financial well-being.
Motor vehicle insurance, an essential expense for many households, increased by 2.4 percent in August, contributing to the overall rise in core inflation. This underscores the importance of monitoring insurance costs, as they can significantly impact consumers' budgets.
The report also highlights disparities in inflation rates among different categories, with notable increases in motor vehicle insurance, while used cars and trucks experienced a decrease. Assessing the factors behind these discrepancies will be crucial for understanding future inflation dynamics.
US Stock Market Reaction
Rising inflation pace (as compared to July 2023) signifies that aggressive quantitative tightening by the Federal Reserve through interest rate hikes is not effective in containing inflation over the long term. The US stock market is under uncertainty, as observed in the Doji candles that emerged on September 13 in both the S&P 500 (the market) and the tech-heavy Nasdaq 100.
Data Source: bls.gov and tradingview.com
Gold Is At An Ideal Buying Level
The Federal Reserve’s higher long-term stance may be an advantage for gold investors.
As the US inflation rate is rising again, it is rendering quantitative tightening by the Fed ineffective. To cage inflation, the Fed has no choice but to keep interest rates high for a longer period. This ‘higher for longer’ scenario will bring more volatility in Treasury yields.
In the short term, when interest rates, as represented by the 10-year US Treasury yield, rise, gold becomes less attractive as an investment compared to interest-bearing assets like bonds. This is because investors can earn higher returns from bonds, making gold, which does not pay interest or dividends, relatively less appealing. As a result, when Treasury yields go up, demand for gold often decreases, causing its price to fall.
Notably, gold is often seen as a hedge against inflation. In the short term, when Treasury yields rise due to concerns about increasing inflation, gold prices may also rise as investors seek to protect their wealth from the eroding effects of inflation. This is because gold is perceived as a store of value that can retain its purchasing power during times of rising prices.
Further, short-term fluctuations in gold prices can also be influenced by market sentiment and risk perception. During periods of uncertainty or economic turmoil, investors may flock to gold as a safe-haven asset, driving up its price even when Treasury yields are rising. Conversely, in times of economic optimism, investors may be less inclined to hold gold, causing its price to fall.
Interestingly, the short-term relationship between gold and Treasury yields can also be affected by the strength of the US dollar. A strong dollar can make gold more expensive for foreign investors, reducing demand and putting downward pressure on its price, even if yields are rising.


Logically, short-term movements in gold prices and Treasury yields can be influenced by speculative trading, technical analysis, and short-term market dynamics. Traders and investors often react to short-term trends, news events, and technical patterns, which can lead to price fluctuations that do not necessarily align with long-term fundamental factors.
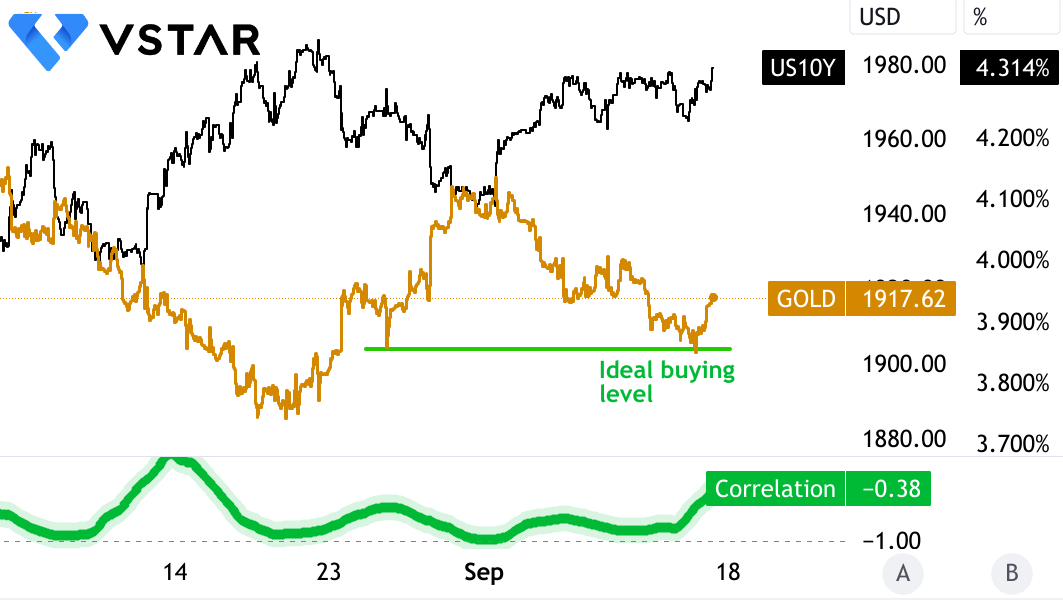
Source: tradingview.com