Oil CFD trading is a popular form of derivative trading that allows investors to profit from the price movements of crude oil without owning the underlying asset. With the potential for high rewards come significant risks, making it essential for traders to understand the basics of the financial markets, risk management strategies, and the principles of technical and fundamental analysis. In this article, we'll explore tips and strategies for successful oil CFD trading, including understanding the advantages and risks, factors affecting the price of oil CFDs, and how to navigate the highs and lows of the market.
Navigating the Highs and Lows of Oil CFD Trading
Oil CFD trading
Oil CFD trading involves the buying and selling contracts for difference (CFDs) that track the price movements of various types of crude oil, such as Brent or WTI. With oil CFD trading, traders can profit from both upward and downward trends in the oil market and can quickly enter and exit trades using online trading platforms.

Advantages and Risks
Advantages of oil CFD trading include the ability to profit from rising and falling prices, leverage that allows for larger position sizes with less capital, and easy access to global oil markets through online trading platforms.
However, risks include the potential for high volatility and losses, market manipulation, counterparty risk with brokers, and a lack of regulatory oversight in some jurisdictions. Traders should carefully manage their positions, use risk management strategies, and choose reputable brokers with transparent pricing and fair trading conditions.

Importance of Understanding the Basics Before Trading
Understanding the basics of trading before engaging in any form of financial trading, including oil CFD trading, is crucial. With a solid foundation of knowledge and understanding, traders can avoid losing money due to a lack of knowledge or poor decision-making. Understanding the basics involves knowing the fundamentals of the financial markets, the principles of technical and fundamental analysis, and risk management strategies. With a firm grasp of these concepts, traders are better equipped to make informed decisions, manage their positions effectively, and avoid costly mistakes. In short, education and preparation are essential for success in oil CFD trading and any other form of trading.
Riding the Market Waves with CFDs: High Rewards, High Risks
What Are CFDs?
CFDs, or Contracts for Difference, allows traders to speculate on the market value movement of an underlying asset without owning it. It's a popular form of derivative trading that enables investors to profit from rising and falling markets. With CFDs, you only need to deposit a small percentage of the total trade value, known as margin, which allows you to leverage your investment and potentially amplify your returns. However, CFDs also come with significant risks, such as high volatility and the potential for substantial losses.
How Do CFDs Work?
CFDs create a contract between the trader and the CFD provider, where the trader speculates on the price movement of an underlying asset. The trader can take either a long position (buy) if they believe the asset price will rise or a short position (sell) if they think it will fall. The CFD provider then calculates the difference between the opening and closing prices of the position, and the trader makes profits or losses based on that difference. CFDs also offer leverage, allowing traders to access more prominent positions with smaller initial capital, but this also increases risk.
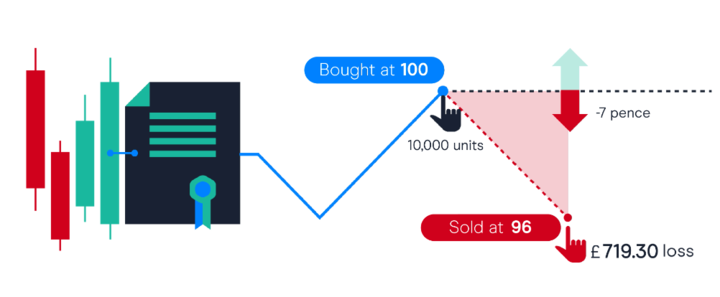
How Are CFDs Different?
CFDs differ from other financial instruments in several ways. Unlike traditional stock trading, CFDs allow traders to speculate on an asset's price moves without owning it, which can result in lower transaction costs. CFDs also offer leverage, allowing traders to open more significant positions with smaller initial capital, which can amplify profits but also magnify losses. Compared to options, CFDs have no expiration date, and traders can hold their positions as long as they wish. However, CFDs carry higher risks due to their leverage and volatility, which makes them unsuitable for some investors.
The Exciting World of Oil CFD Trading
Oil CFD trading
Oil CFD trading refers to the practice of buying and selling contracts for difference (CFDs) based on the price fluctuations of crude oil. Traders can profit from the difference in the price of the CFDs.
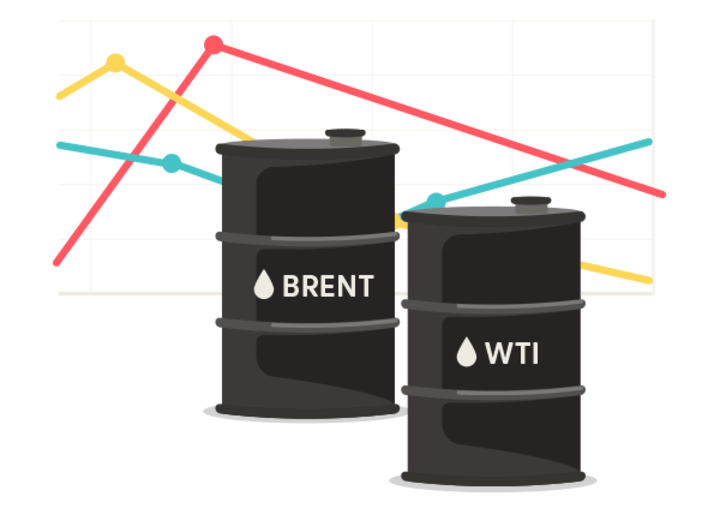
Types of Oil CFDs
There are two main types of oil CFDs. The first type is Brent crude, extracted from the North Sea and used as a benchmark for global oil prices. The second type is West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude, a high-quality oil extracted from the United States and serves as a benchmark for North American oil prices. Traders can buy or sell these CFDs and profit from the price difference over time.
Advantages of Trading Oil CFDs
Trading oil CFDs has several advantages, including accessibility, flexibility, and profit potential. CFDs allow traders to gain exposure to oil prices without owning the underlying asset, making it a more accessible and affordable option.
Additionally, traders can take advantage of both upward and downward price movements by buying or selling CFDs. The flexibility to trade CFDs 24/7 also provides opportunities to react quickly to market events. With the potential for high leverage and to breed profit from both rising and falling markets, oil CFDs offer traders the potential for significant gains.
Risks of Trading Oil CFDs
Trading oil CFDs also comes with risks. As with any form of leveraged trading, traders can potentially lose more than their initial investment. The high volatility of oil prices can lead to significant price movements that can be difficult to predict, and market events such as political instability or natural disasters can cause sudden and unexpected price swings.
Furthermore, oil prices can be influenced by factors beyond the control of traders, such as supply and demand fundamentals, leading to market volatility. Therefore, traders must be aware of these risks and implement appropriate risk management strategies to limit their exposure.
Factors Affecting the Price of Oil CFDs

Several factors can impact the price of oil CFDs, including supply and demand, geopolitical events, economic indicators, and weather patterns. Any disruption in the global supply chain or unexpected increase in demand can lead to a rise in prices. Similarly, political tensions, wars, or conflicts in oil-producing countries can create supply shortages, leading to higher prices.
Additionally, economic indicators like GDP and unemployment rates can influence oil prices as they reflect the overall health of the global economy. Lastly, weather patterns, such as hurricanes or droughts, can impact oil production and transportation, affecting prices.
How to Trade Oil CFDs
Choosing a Broker
When trading oil CFDs, it's essential to choose a reputable broker that offers competitive spreads and reliable execution. Look for a broker regulated by a reputable authority, offers a user-friendly trading platform, and provides access to a range of oil markets and trading instruments. Additionally, check the broker's fees, funding and withdrawal options, and customer support. With the right broker, traders can speculate on the price movements of oil contracts without owning the underlying asset.
Register and Deposit
To trade oil CFDs, you'll need to register with a broker and make a deposit. First, fill out the broker's registration form and provide the required personal and financial information. Once your account is approved, you can deposit funds using various payment methods, such as credit or debit cards, bank transfers, or e-wallets. The minimum deposit requirement varies by broker. Once the account is funded, you can start trading oil CFDs by selecting the desired contract, entering your trade size, setting your stop-loss and take-profit levels, and executing the trade.

Opening and Closing Trades
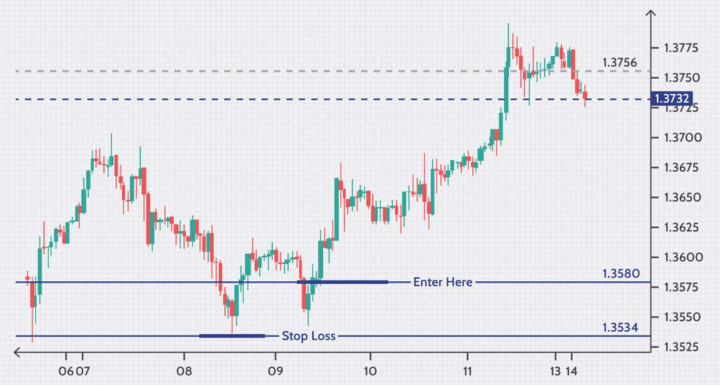
To open a trade in oil CFDs, you'll need to select the desired contract, choose the position (long or short), enter the trade size, and set your stop-loss and take-profit levels. Once you're ready to execute the trade, click the buy or sell button.
To close a trade, you can either set a take-profit level to automatically close the trade at a profit or use the platform's close button to manually exit the trade. Keep in mind that oil prices can be volatile, so it's essential to monitor your transactions closely and adjust your stop loss levels as needed.
Managing Risk and Controlling Losses
Managing risk is crucial when trading oil CFDs to minimize potential losses. Traders can use various risk management tools, such as stop loss orders, to limit their potential losses. A stop-loss order automatically closes the trade if the price reaches a predetermined level, protecting traders from significant losses in the event of an unexpected price movement.
Additionally, traders can use position sizing to limit their exposure to the market and avoid taking on excessive risk. It's also essential to monitor the market closely and adjust stop loss levels as needed to ensure that potential losses are controlled.
Strategies For Trading Oil CFDs
There are numerous trading strategies that traders can use when trading oil CFDs. One popular strategy is trend following, which involves identifying the market direction and tracking it. This strategy can be used with technical analysis tools like moving averages, trendlines, and chart patterns. Traders can use these tools to identify support and resistance levels and enter trades in the direction of the trend when prices break through these levels.
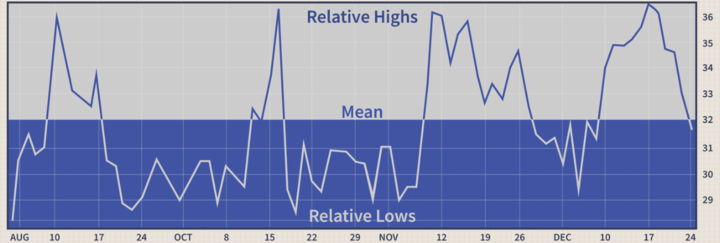
Another strategy is mean reversion, which involves looking for opportunities to buy or sell oil CFDs when prices deviate significantly from their historical averages. This strategy is based on the assumption that prices come back to the mean over time. Traders can use technical indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) to identify oversold or overbought market conditions and then enter trades in the opposite direction of the trend.
Notably, News trading is another popular strategy, where traders analyze the impact of market news and events on oil prices and use this information to take advantage of short-term price movements. For example, if a major oil-producing country announces that it will increase production, traders might expect prices to fall and enter short trades.
Apart from that, Swing trading is another popular strategy for oil CFD traders. This involves holding positions for several days to take advantage of short-term price fluctuations. Traders can apply technical analysis to identify support and resistance levels and enter trades when prices bounce off these levels.
Ultimately, the key to successful oil CFD trading is to develop a well-defined strategy, manage risk effectively, and adapt to changing market conditions.
Why Trade Forex With VSTAR?
Forex trading with VSTAR is a wise decision due to its full regulation and institutional-level trading costs. VSTAR is authorized and regulated by the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission, providing a secure and trustworthy platform for trading. They offer low trading fees, super tight spreads, and deep liquidity, ensuring reliable and fast order execution.
Furthermore, their user-friendly App caters to professional traders and beginners, with a minimum deposit of only $50 and negative balance protection. By choosing VSTAR, traders can trade confidently and take advantage of the vast array of markets and payment methods available.
Essential Tips For Successful Oil CFD Trading
Oil CFD trading can be a profitable venture, but it requires discipline, strategy, and attention to market trends. One crucial tip for successful oil CFD trading is to stay informed and up-to-date with the latest news and events impacting the oil market. This includes monitoring supply and demand trends, political developments, and economic indicators that may affect oil prices.
Another important tip is to have a well-thought-out trading plan and stick to it. A trading plan should include entry and exit points, risk management strategies, and profit targets. It's also essential to avoid emotional trading and stick to the plan regardless of market conditions.
Risk management is a critical component of successful oil CFD trading. Traders should use stop-loss orders and position-sizing techniques to limit their risk and minimize losses. It's essential to be disciplined and avoid over-leveraging positions, as this can lead to significant losses.
Conclusion
Summary Points
● Oil CFD trading involves buying and selling contracts that track the price movements of crude oil.
● Traders can profit from upward and downward trends and quickly enter and exit trades online.
● Advantages include leverage, the ability to benefit from both price directions and easy access to global oil markets.
● Risks include potential losses, market manipulation, and counterparty risk.
● Understanding the basics before trading is crucial, involving knowledge of financial markets, technical and fundamental analysis, and risk management.
● Oil CFDs differ from other financial instruments, and factors affecting prices include supply and demand, geopolitical events, economic indicators, and weather patterns.
In conclusion, oil CFD trading can be a favorable opportunity for traders who have a good understanding of the oil market and the factors that affect oil prices. It gives traders the flexibility to go long or short, leverage their positions, and trade oil without owning the underlying asset. However, it is a high-risk investment, and traders must be prepared to manage their risk effectively. By using technical and fundamental analysis, setting stop-loss orders, and monitoring the market closely, traders can make profits in oil CFD trading.
FAQs
How do I start trading oil CFDs?
To start trading oil CFDs, you will need to find a reputable online broker that offers CFD trading on oil, open a trading account, and deposit funds into it. Once you have done that, you can start trading oil CFDs by selecting the oil contract you want to trade, specifying the trade size, and opening the position.
What are the trading hours for oil CFDs?
Trading hours for oil CFDs depend on the exchange on which the underlying asset is traded. Typically, oil CFDs can be traded 24/5, meaning they are available for trading 24 hours a day from Monday to Friday.
Can I trade oil CFDs on mobile devices?
Many online brokers offer mobile trading platforms that allow you to trade oil CFDs on the go. VSTAR has a mobile app that supports oil CFD trading. However, it is essential to note that trading on mobile devices may carry additional risks, such as poor connectivity and difficulty monitoring the markets.
*Disclaimer: The content of this article is for learning purposes only and does not represent the official position of VSTAR, nor can it be used as investment advice.