What is A Trading Plan?
A Forex trading plan is an established strategy that guides traders' analyses and executions in the market. It helps you (like other market participants) remain net profitable. However, not every trading plan is similar.
Each forex trader has different opinions, backgrounds, and risk tolerance. Therefore, it is best to have your trading plan and stick to it no matter what.
Importance of Having a Trading Plan
Experts never advise anyone to trade without a solid trading plan because you could miss the following benefits:
● Profitable trades: As discussed, the best trading plan promotes profitable results through sound market assessments, executions, and risk management.
● Objective decision-making: When money is at risk, you can make emotional decisions that you may regret later. A proper trading plan template reduces such chances.
● Less confusion: Beginners can quickly get confused without a strategy due to the hundreds of Forex charts available, but trading becomes easy with an arranged plan.
Identifying The Goals With Of Your Trading Plan
An outstanding Forex trading plan starts with you. Why have you become a trader? How do you foresee your growth? What are your goals?
Setting specific long-term goals helps you work out a plan to achieve them. Then, you can divide the targets into intermediate- and short-term ones to measure your progress continuously.
For example, you may aim for a monthly profit of 5%, trading only major currency pairs (e.g., EURUSD and USDCHF). That means you'll need less than a 1% return of your account size every week to achieve it.
It will compound into a 60% gain at this rate by the year's end. However, it's important to always remain realistic with such targets, especially as a beginner.
The goals will then help you identify a trading style that should be unique to you.

One of the most significant aspects of such a trading style is your risk tolerance. It is the extent of loss you are comfortable taking whenever executions go against you.
They are all part of the trading plan you must produce and obey because deviation from it may hurt your goals.
Conducting Market Analysis
After defining your goals, analyzing the market to understand its underlying conditions (trends) is the next step to planning, testing, or executing any trading plan.
They can be short-, intermediate-, or long-term trends in the following categories:
● Uptrend: The price moves up with momentum making new highs, and any fall is brief & temporary.
● Downtrend: The exchange rate falls for a long time in a downtrend.
● Sideways/Horizontal trend: During sideway trends, the price keeps moving back and forth within a range.
Below are examples of an uptrend and a downtrend:
Only you can determine the best market conditions for your plan. However, experienced traders advise against trading during a sideways trend because it is uncertain.

The time horizon (M1, M5, H1, D1, etc.) also largely depends on you and your goals, as discussed.
Understanding Market Volatility
The Forex market is never stable in price, especially throughout weekdays when it is open. Regardless, such volatility is responsible for your profits (and losses) by predicting its next direction.
The larger and more frequent the price swings, the more volatile a currency pair is. Thus, you may want to trade less volatile ones to be safer.
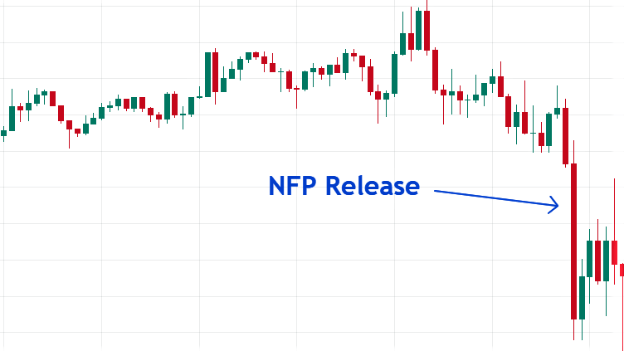
Moreover, major news reports increase price volatility significantly. One example is the Non-Farm Payroll (NFP) release on the first Friday of every month.
Below is an example of its effect in a USDCAD chart:
Developing a Trading Method For Your Plan
Becoming profitable by forex trading becomes more likely with a proper trading method. Several kinds exist based on various factors, but they are usually within these categories:
● Scalping: Scalping is a strategy to gain very few pips within seconds to minutes multiple times throughout a trading day.
You hardly look beyond the one-hour time frame for direction bias while using 1-minute or 5M charts for entry.
● Day trading: A day trading plan involves opening and closing trades within a day. No forex order stays overnight.
For example, day traders could observe the daily chart to determine the trend and execute orders on the 15-minute or 30-minute charts.

● Swing trading: Unlike day trading, a swing trading plan demands leaving orders open for a few days to weeks.
The monthly charts usually help swing traders understand the current trend before taking trades on the 1-hour or 4-hour charts.
● Position trading: Position trading is the longest of all trading methodologies, as a trade may last for months to years.
Position traders use 4-hour, daily, and weekly charts to enter such trades.
● Trend following: Trend following traders buy or sell currencies when the price is in a clear uptrend or downtrend.
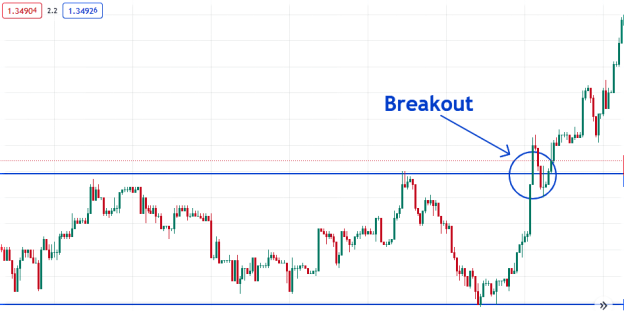
● Breakout trading: This method involves taking trades when the price moves outside a support or resistance level.
For example, a breakout trader may open a buy order when the price significantly breaks above the range shown below.
How To Select a Method That Resonates With Your Trading Style
Each or combination of the methods above can yield success. However, how do you choose the best?
● Determine and assess your goals as soon as possible to determine what type of trader you will be.
● Calculate and prepare for the risks involved in your choices. For example, swing traders will be more open to more losses in pips than a scalper because they use a higher time frame.
● Analyze yourself carefully to know your preferences. For instance, if you are not patient or can't focus for too long, a lower time frame trading plan may be the best for you, and vice-versa.
● Improve on your strengths and (especially) weaknesses because you can't allow feelings to influence your decisions. An objective mindset is essential for forex trading success.

Implementing a Method That Suits Your Trading Goals
Whatever your trading method(s) is, as discussed earlier, it will be in one of the primary classes of market analyses below:
● Fundamental analysis: Fundamental analysts will implement their method based on the outcome of real-world events. They frequently keep up with financial reports and anticipate upcoming events on economic calendars.
As the NFP example shared earlier, fundamental analysis may help traders expect the outcome before its release to profit from it.
● Technical analysis: Technical analysis involves utilizing tools on a trading platform to identify patterns, trends, and support & resistance points. The tools can be simple, like regular lines for support/resistance. They can also be complex like overbought/oversold indicators.
Regardless of your preferred trading method, you must evaluate its performance frequently through back and forward tests. Such tests will reveal adjustments (whether big or small) to make to reach your goals better.
Developing a Risk Management System
No trading strategy, whether forex or even a stock trading plan, is ever complete without an ideal method to manage risks.
It's always advisable to control how much you are willing to lose for some potential profit. In the same way, you can also try to maximize the gains when possible.
Whatever approach you've devised to tackle these and include in your Forex trading plan, stop-loss and trailing stop are some of the most helpful market orders.
Ensure you learn to measure and set them smoothly on your trading platform.
Building A Trading Strategy
A forex trading plan may sound too complex and even unnecessary to new traders because it may be challenging to build. However, that's not always the case.

You can develop (and write down) excellent strategy rules following this checklist:
1. Find favorable currency pairs: There are several currency pairs in the forex market. Thus, you should specify those you will be trading for solid reasons.
For example, you may prefer to trade EURUSD and USDCHF because they are some of the least volatile pairs.
2. Identify the best market conditions to trade: After selecting the pairs that interest you, understanding their market conditions is the next step. Is the price trending up or down, or is it ranging? You will likely prefer trading during trending conditions.
3. Know your preferred time horizon: Various factors will determine your best time horizon, but ensure you note this in your strategy.
For instance, you may be a college student who doesn't have all day to stare at price charts. Hence, a trading plan template with a day or swing strategy makes more sense.
4. Look out for economic reports: Before entering trades, check for any upcoming economic releases. Major news affects the price significantly and can lead to losing trades.
5. Understand your entry strategy: What do you want to see before opening market orders? Do you prefer to buy above a support level and sell below a resistance? Should indicators confirm price action first?
Verify and write down rules on how you prefer to enter trades.
6. Implement your risk management rules: After confirming an entry signal, estimate and be comfortable with the amount you're risking. Usually, experts recommend only 2-3% of your account size.
Use position sizing calculations to understand how many lots you should buy or sell. Also, your risk-reward ratio will determine where to place stop loss and take profit orders in every trade.
7. Note your exit techniques: If the price doesn't trigger your stop loss or take profit orders, how else do you want to exit trades?
You should have an established strategy to close trades.
In the end, always ensure you are on track with your goals. Often analyze statistics like your win/loss ratio and average profit or loss per trade to learn new ways to improve.
Your trading plan will be the most profitable for you soon.
Measuring Market Volatility
Forex market volatility may seem a disadvantage and even discourage new traders. But it's impossible to be profitable if the price remains stagnant.
Remember, the essence of forex trading is predicting price movement through various analyses. Therefore, you must consider volatility’s impact when building any forex or even stock trading plan.
There are two widely-accepted types of market volatility:
● Historical Volatility: Historical volatility measures an asset's price back-and-forth movement in the past. It doesn't provide details about future fluctuations, but you can learn how to calculate it through this comprehensive WikiHow guide.
● Implied Volatility: Implied volatility (IV), on the other hand, shares possible details about future price movements. A higher IV signifies massive price swings are coming and vice-versa.
Setting Risk Management Rules
Proper risk management is the backbone of the best trading plan template because you can be profitable without solid analysis skills.

One of the most crucial aspects of this management is your risk-reward ratio per trade.
It is the amount you're willing to lose for the amount you could gain. For example, a risk-reward ratio of 1:3 means you're ready to lose $10 for $30 or $100 for $300.
To ensure this, you must set a stop-loss and target profit order on every trade.
Understanding Position Sizing
Position size in forex is the amount of currency pair units a trader wants to invest in. It is vital to calculate your limit correctly to align with your risk tolerance.
Its basic formula per trade is dividing an account risk by the trade size. However, the calculation may be complex for a beginner.
In a trading plan example, a trader may be willing to risk only 2% of a $10,000 account, which is $200. If the trader decides to place a stop loss of 250 pips per trade, the risk value per pip will be $0.8.
Therefore, when trading a currency pair like EURUSD with a 10,000 pip value ratio, the position sizing will be $0.8 * 10,000 = 8,000 units of EURUSD.
Testing and Optimizing Your Strategy
Building a trading strategy is one thing; ensuring it works is another. There's no point in having a plan that isn't profitable, so you need to test it thoroughly in the following ways:
● Backtesting: Backtesting means verifying if your strategy would have worked in the past by using historical price data. Some traders automate their strategy for this, but you can manually observe the charts yourself.
● Forward testing: By forward testing (or paper trading), you are trading in a simulated or demo account with real-time conditions.
You can identify possible weaknesses in your trading strategy during these tests and fine-tune them for the better.
For example, your strategy rule for entering buy trades may have been to wait for candlesticks to move above a rising Moving Average. However, during the tests, you may discover that using more than one Moving Average on a chart gives more accurate signals.
You can then adjust the strategy to include the discovery.
Testing Your Trading Plan
As discussed, you can't be sure your trading plan will be profitable after building it. Therefore, you need an excellent demo account to backtest and forward test.
VSTAR Demo is one of the most reliable providers to enjoy live market conditions for this.
You will get the fastest market insights and access to every trading tool free of charge. If you prefer to automate the strategy, the trading platform runs smoothly and is easy to use on any device.
Moreover, VSTAR's free educational resources can guide in building a solid trading plan for beginners.
Evaluate the test results and refine your plan to become its best version!
Implementation and Execution
After carefully testing your plan to prove it is profitable enough, you can decide when to use it under live market conditions.
There are no harsh rules about this because everyone's strategy should differ except you copied another's trading plan pdf. Regardless, remember that the process must align with your goals. It should contain every detail about when and how to engage and leave in the market.
Every rule must be precise, with no chance for emotions to affect your decisions. If you can, automate your strategy to reduce engagement.
As you gain more experience in the market, you will see the need for regular improvements. Make such adjustments quickly but correctly.
Conclusion
Every trader hoping for success has goals, which likely involve remaining profitable for as long as possible. A trading plan helps achieve them.
To develop a successful trading plan, you need to understand the following:
● The most favorable market conditions for you
● How you can enter and exit trades profitably
● Your risk tolerance
Lay down rules based on them and implement the plan on a demo account to confirm its success.

The best trading plan for beginners is simple and clear to reach your goals. Yet, as your experience improves in the market, you may need to improve it regularly.
*Disclaimer: The content of this article is for learning purposes only and does not represent the official position of VSTAR, nor can it be used as investment advice.




