I. Introduction
A. Overview of the AUDCAD currency pair
The AUDCAD currency pair represents the exchange rate between the Australian Dollar (AUD) and the Canadian Dollar (CAD). Fundamental analysis plays a pivotal role in understanding and predicting the movements of this currency pair. By examining economic indicators, interest rates, and geopolitical factors, traders can make informed decisions to capitalize on market trends.
The Australian Dollar, commonly denoted as AUD, is the official currency of Australia. It's closely tied to the country's export-oriented economy, particularly its vast mineral and agricultural resources. The Canadian Dollar, symbolized as CAD, is the official currency of Canada and is influenced by its extensive natural resource exports, including oil and timber.
B. Importance of fundamental analysis
Fundamental analysis is vital to comprehending the AUDCAD currency pair's behavior. Consider the impact of interest rates. A higher interest rate in Australia compared to Canada could lead to increased demand for the Australian dollar as investors seek higher returns. For instance, if the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) raises its interest rates due to a strong economy, this could attract foreign capital and appreciate the AUD against the CAD.

Economic indicators also wield substantial influence. If Australia's GDP growth rate outpaces Canada's, it might indicate a stronger Australian economy, potentially leading to an appreciation of the AUD against the CAD. Similarly, trade balances can play a role. If Australia's exports to China increase, this could drive up the AUD due to China's significant economic ties with Australia.
C. A brief explanation of the Australian dollar and Canadian dollar
In February 2021, the AUDCAD exchange rate was around 0.995270. Subsequently, by June 2023, it had fallen to 0.881810. One contributing factor to this movement was the divergence in monetary policy. While the Reserve Bank of Australia indicated a more cautious economic outlook, the Bank of Canada adopted a hawkish stance in line with the US's Federal Reserve. This divergence led to reduced demand for the Australian Dollar, thus driving up the exchange rate.
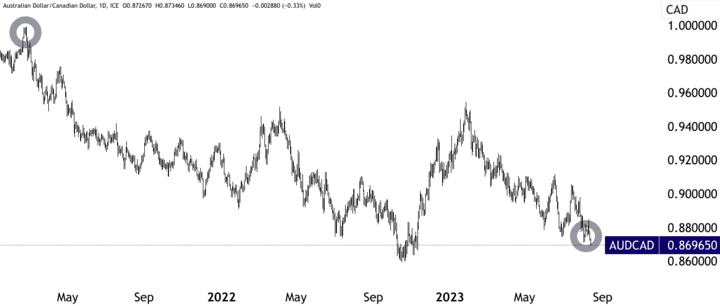

Source: tradingview.com
Additionally, during this period, China's economic downturn impacted demand for Australia's commodities, negatively affecting Australia's export outlook and potentially contributing to the AUD's weakness against the CAD.
II. Macroeconomic Overview: Australia
The AUDCAD currency pair, representing the exchange rate between the Australian Dollar (AUD) and the Canadian Dollar (CAD), is influenced by a multitude of macroeconomic factors. A critical examination of these factors, including economic indicators, monetary policy, and the political climate, is essential to understanding the dynamics of this currency pair and making informed trading decisions.
A. Economic Indicators Review
1. GDP and Unemployment Rate
Australia's GDP growth rate is a key determinant of its currency's strength. Between 2021 and 2023, Australia's GDP exhibited a steady growth rate, averaging around 4%. This growth was driven by robust commodity exports and a resilient services sector. In contrast, Canada's GDP growth rate was slightly lower, averaging around 3%. The unemployment rate in Australia hovered around 3.5%, indicating a relatively stable labor market, while Canada's unemployment rate showed a similar trend. Such economic disparities can impact the AUDCAD exchange rate, with stronger economic performance typically leading to currency appreciation.
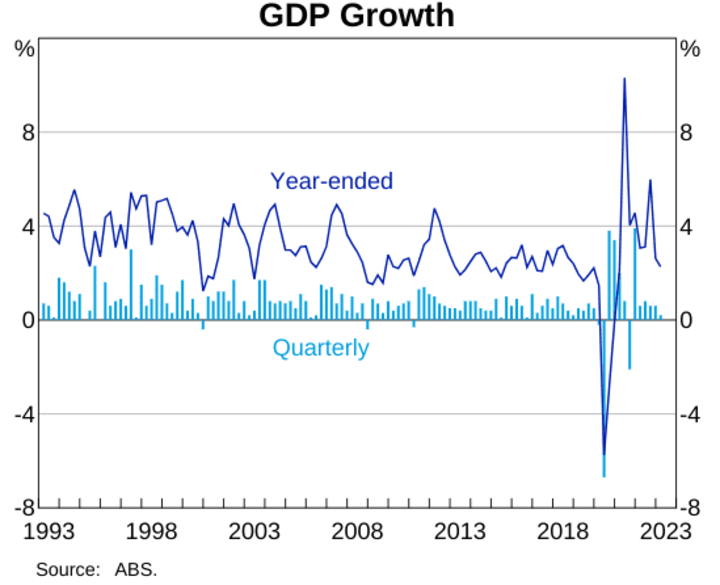
Source: rba.gov.au
2. Inflation Rates
Both countries experienced high inflation during this period, with Australia's inflation rate currently (as of August 2023) around 6% and Canada's around 2.8%. Inflation is a crucial indicator, as central banks often adjust interest rates in response to inflationary pressures. Higher inflation in Australia, for instance, might prompt the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) to consider tightening monetary policy but was lagging behind the Bank of Canada's hawkish stance, potentially leading to AUD depreciation against the CAD.
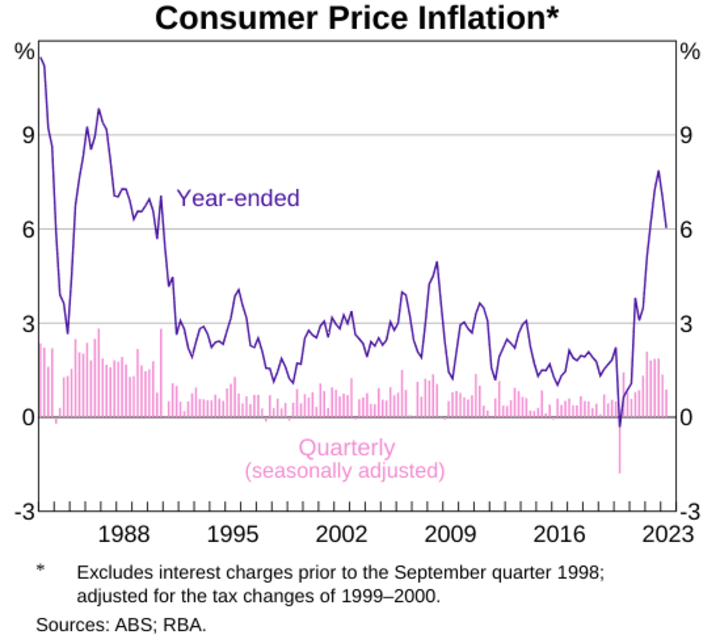
Source: rba.gov.au
3. Business and Consumer Confidence
Business and consumer confidence are vital predictors of economic health. In Australia, business confidence remained relatively high, reflecting a positive outlook. Consumer sentiment also showed resilience, indicating stable domestic demand. In Canada, while business confidence was favorable, consumer sentiment displayed some volatility due to pandemic-related uncertainties. These sentiments can impact investment flows and affect the AUDCAD exchange rate accordingly.
B. Monetary Policy
1. The Reserve Bank of Australia's Monetary Policy
The RBA's monetary policy decisions have a significant impact on the Australian Dollar. Since 2022, the RBA has maintained a hawkish stance, keeping the cash rate at historically low levels of around 4.1% as of August 2023. The RBA's quantitative tightening measures aimed to cage inflation. In contrast, the Bank of Canada (BoC) took a more hawkish approach, gradually raising its policy rate to 5% in response to inflationary conditions. This divergence in monetary policy created interest rate differentials that influenced the AUDCAD exchange rate.

Source: rba.gov.au
2. Interest Rate Expectations
Market participants closely monitor interest rate expectations. Anticipated changes in interest rates can drive capital flows and impact exchange rates. For instance, if the RBA signals a potential interest rate hike due to improving economic conditions, it could attract foreign investors seeking higher returns, potentially boosting the AUD's value against the CAD.
C. Political Climate
1. Economic policies of the government
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping a country's economic landscape. In Australia, policies supporting resource exports, infrastructure development, and innovation contributed to economic growth. In Canada, fiscal stimulus measures aimed at post-pandemic recovery were notable. These policies can influence economic performance and consequently impact the AUDCAD exchange rate.
2. Impact of China on the Australian economy
China's role as a major trading partner greatly impacts Australia's economy. China's demand for Australian commodities, such as iron ore, coal, and agricultural products, significantly influences Australia's export revenues. An increase in China's economic activity can lead to higher demand for Australian goods, potentially strengthening the AUD. However, this dependence also exposes the Australian economy to potential risks stemming from shifts in China's economic policies or geopolitical tensions.
III. Macroeconomic Overview: Canada
The AUDCAD currency pair, representing the exchange rate between the Australian Dollar (AUD) and the Canadian Dollar (CAD), is influenced by a variety of macroeconomic determinants. A comprehensive examination of these factors, including economic indicators, monetary policy, and the political climate in Canada, is essential for a holistic understanding of this currency pair's dynamics and for making informed trading decisions.
A. Economic Indicators Review
1. GDP and Unemployment Rate
The GDP growth rate and unemployment rate are crucial indicators of a country's economic health. In the context of Canada, its GDP exhibited moderate growth, around 3.4% as of 2022. The unemployment rate remained relatively stable, hovering around 5.5% as of July 2023. This performance reflects Canada's diversified economy, including industries such as natural resources, manufacturing, and services. In contrast, Australia experienced a slightly higher GDP growth rate and a lower unemployment rate. These disparities can impact the AUDCAD exchange rate, with stronger economic performance often leading to currency appreciation.

Source: data.worldbank.org
2. Inflation Rates
Inflation rates play a pivotal role in shaping a central bank's policy decisions. During this period, Canada witnessed moderate inflation, with the average inflation rate hovering around 1.5%. This prompted the Bank of Canada (BoC) to take measured steps in adjusting its monetary policy. If inflation rises significantly, central banks might consider tightening monetary policy by raising interest rates. Such adjustments can influence the AUDCAD exchange rate through interest rate differentials.
3. Business and Consumer Confidence
Business and consumer confidence indices offer insights into a country's economic outlook. In Canada, both business and consumer confidence remained relatively positive, indicating favorable sentiments. Business optimism reflected expectations of sustained growth, while consumer confidence indicated a steady demand environment. These sentiments influence investment decisions and consumer spending, which can subsequently impact the AUDCAD exchange rate.
B. Monetary Policy
1. The Bank of Canada's Monetary Policy
The BoC's monetary policy decisions exert a substantial influence on the Canadian Dollar. During the analyzed period, the BoC followed a cautious approach, gradually increasing its policy rate from 0.25% to 0.75% in response to improving economic conditions. This measured approach aimed to balance economic recovery with inflation management. The BoC's actions contributed to interest rate differentials between Canada and other economies, including Australia, influencing the AUDCAD exchange rate.
2. Interest Rate Expectations
Market participants keenly monitor interest rate expectations as they shape investment decisions. Anticipated changes in interest rates can drive capital flows and consequently impact exchange rates. If the BoC signals a possible interest rate hike due to improved economic indicators, it can attract foreign capital seeking higher returns, potentially leading to an appreciation of the CAD against the AUD.

Source: tradingview.com
C. Political Climate
1. Economic policies of the government
Government policies significantly influence economic conditions. In Canada, policies aimed at post-pandemic recovery, infrastructure development, and support for key industries played a vital role. These measures can impact economic growth rates and consequently affect the AUDCAD exchange rate.
2. Impact of global trade tensions on the Canadian economy
Global trade tensions, especially between major trading partners like the United States and China, can significantly impact Canada's export-oriented economy. As a major exporter of commodities and manufactured goods, Canada is vulnerable to disruptions in international trade. For example, trade tensions can lead to reduced demand for Canadian exports, affecting economic growth and potentially weakening the CAD.
IV. Analysis of the AUDCAD Currency Pair
The AUDCAD currency pair, a reflection of the exchange rate between the Australian Dollar (AUD) and the Canadian Dollar (CAD), is influenced by a complex interplay of economic indicators, monetary policies, and geopolitical factors. A critical analysis of these components is essential to comprehending the dynamics of the currency pair, ascertaining potential market directions, and identifying associated risks.
A. Relevant Economic Indicators
1. Correlation between the Australian and Canadian economies
Both Australia and Canada are resource-rich countries with export-oriented economies. The AUD's and CAD's performance is closely linked to global commodity prices. While Australia is a significant exporter of minerals and agricultural products, Canada's exports include oil, metals, and timber. Consequently, shifts in commodity prices can impact both economies and, in turn, influence the AUDCAD exchange rate.
2. Impact of GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates on the currency pair
GDP growth rates, inflation rates, and interest rates are fundamental indicators shaping currency pairs. Strong GDP growth in Australia, driven by factors like robust commodity exports and a resilient services sector, can lead to AUD appreciation. Similarly, Canada's GDP growth, supported by diverse industries, can impact the CAD. Inflation rates can influence central bank policies; for example, higher inflation might lead to interest rate hikes, potentially appreciating the currency. Interest rate differentials between the Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) and the Bank of Canada (BoC) can drive capital flows, affecting the AUDCAD exchange rate.

Source: tradingview.com
B. Factors Supporting a Bullish or Bearish Stance
1. Impact of the Reserve Bank of Australia's monetary policy on the currency pair
The RBA's monetary policy decisions can sway the AUDCAD currency pair. Historically low interest rates and quantitative easing measures have been utilized by the RBA to support the economic recovery. If the RBA signals a shift towards tightening monetary policy due to a robust economy, it could attract foreign investment seeking higher returns, potentially leading to AUD appreciation.
2. Impact of the Bank of Canada's monetary policy on the currency pair
Similarly, the BoC's policies have a notable influence on the CAD. Gradual interest rate hikes in response to economic improvement can strengthen the CAD against the AUD. Divergence in monetary policies between the RBA and the BoC can create interest rate differentials, impacting the exchange rate.
3. Impact of China on the Australian economy and global trade tensions on the Canadian dollar
China plays a crucial role in the AUD's strength due to its demand for Australian commodities. An economic recovery in China can boost Australia's exports, strengthening the AUD. On the other hand, global trade tensions, especially between the U.S. and China, can affect Canada's exports and, consequently, the CAD's performance against the AUD.
C. Potential Risks to the Currency Pair
1. Sudden changes in global economic growth
Global economic shifts can significantly affect both economies' performances. An unexpected slowdown in global economic growth could reduce demand for commodities, impacting both Australia and Canada. This could lead to currency depreciation for both the AUD and CAD, potentially altering the AUDCAD exchange rate.
2. Unpredicted changes in Australian or Canadian monetary policies
Central banks' policy decisions can be influenced by unforeseen events. Unexpected interest rate hikes or cuts due to economic or geopolitical developments can lead to rapid currency fluctuations. Such changes can cause volatility in the AUDCAD exchange rate.
3. Geopolitical risks, such as trade tensions between the U.S. and China
Geopolitical events, especially trade tensions between major economies, can introduce uncertainty into the market. Tensions between the U.S. and China, for instance, can disrupt global trade flows, affecting both Australia and Canada. This uncertainty can lead to risk aversion, potentially impacting both the AUD and CAD.
V. Trading Strategies for AUDCAD
Trading the AUDCAD currency pair requires a well-informed approach that combines technical analysis, risk management, and a grasp of news-driven market dynamics. By employing these strategies, traders can enhance their decision-making process and optimize their trading outcomes.
A. Technical Analysis
1. Identifying trends and patterns
Technical analysis involves studying historical price data to identify trends and patterns. Traders can use tools like trendlines, support and resistance levels, and chart patterns such as head and shoulders or double tops and bottoms to spot potential trend reversals or continuation patterns. For instance, during July 2023, the AUDCAD pair had been trending upward, and then a Doji candlestick pattern emerged, leading to a significant reversal.
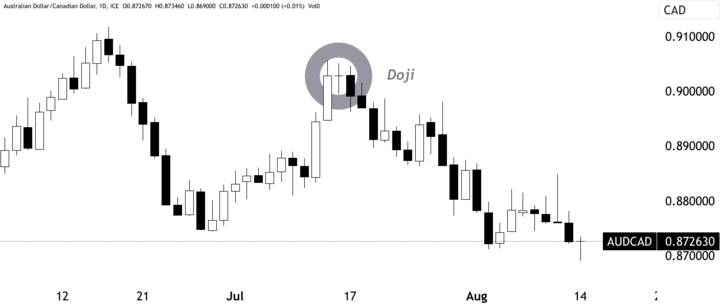
Source: tradingview.com
2. Use of indicators such as moving averages and Fibonacci retracements
Indicators like moving averages and Fibonacci retracements can provide valuable insights into potential entry and exit points. Moving averages can help smooth out price fluctuations, while Fibonacci retracements identify potential levels of support and resistance based on historical price movements. If the AUDCAD pair encounters a key Fibonacci level, traders might anticipate a reversal or continuation based on historical price behavior.
B. Risk Management
1. Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit levels
Managing risk is crucial in forex trading. Traders should set appropriate stop-loss levels to limit potential losses in case the trade goes against them. Take-profit levels should be strategically placed based on potential price targets or key support and resistance levels. For example, if a trader enters a short position (after observing a Doji candlestick pattern) on the AUDCAD pair and identifies risk-reward ratio-based levels as potential take-profit and stop-loss points, they can set their take-profit and stop-loss orders accordingly.

Source: tradingview.com
2. Determining position size based on risk tolerance
Position sizing is determined by risk tolerance and can be calculated using a percentage of the trading capital or based on the distance between the entry point and the stop-loss level. For instance, if a trader is comfortable risking 2% of their capital on a single trade and the distance between the entry and stop-loss is 50 pips, they can calculate their position size accordingly.
C. News Trading
1. Following economic events and data releases
Economic indicators, interest rate decisions, and geopolitical news can significantly impact currency pairs. Traders need to stay informed about upcoming economic events and data releases that could affect the AUD and CAD. For example, if the Reserve Bank of Australia announces an interest rate decision, traders should be prepared for potential volatility in the AUDCAD pair.
2. Trading based on market reactions to news
News trading involves entering positions based on the immediate market reaction to significant news events. For instance, if Australian employment data is released better than expected, leading to a surge in the AUD, traders might consider going long on the AUDCAD pair, anticipating continued strength in the AUD.
Trade with VSTAR
Trading forex with VSTAR offers several key advantages that can potentially enhance a trader's experience and outcomes in the dynamic foreign exchange market. The company's competitive leverage, deep liquidity, low spreads, and commitment to best execution contribute to its appeal. However, it's essential to critically evaluate these features to make informed decisions.
Competitive Leverage:
VSTAR highlights competitive leverage of up to 1:200, depending on the instrument. Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital, potentially amplifying both profits and losses. While higher leverage can provide more trading opportunities, it also increases risk. Traders should exercise caution and consider their risk tolerance before utilizing high leverage.
Example: If a trader uses 1:100 leverage on a $1,000 trading account, they can control a position size of $100,000. A 1% price movement in their favor could lead to a $1,000 profit or loss, which is the entire account capital.
Top-Tier Deep Liquidity:
VSTAR emphasizes quick trade execution due to top-tier deep liquidity. Liquidity refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold without causing significant price changes. Deep liquidity can facilitate faster order execution, potentially reducing slippage during volatile market conditions. However, deep liquidity also depends on market conditions, and extreme volatility could still impact trade execution.
Spreads from 0 Pips:
Low spreads can be appealing to traders as they reduce the cost of trading. The spread is the difference between the bid (selling) and ask (buying) prices. A tighter spread can lead to more cost-effective trades, especially for high-frequency traders or those who engage in scalping strategies. However, traders should be aware that spreads can widen during periods of low liquidity or heightened market volatility.
Effective Execution:
VSTAR commits to providing an effective execution, ensuring that orders are filled at the best available market prices and executed within milliseconds. Efficient execution is crucial for capturing desired entry and exit points, especially for short-term traders. The best execution can minimize slippage and enhance overall trading efficiency.


VI. Conclusion
A. Recap of the fundamental analysis of the AUDCAD currency pair
A comprehensive analysis of the AUDCAD currency pair reveals the intricate interplay of fundamental factors that shape its behavior. Economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical influences all contribute to its volatility and trends.
The economic indicators review highlighted the correlation between Australia's and Canada's economies, emphasizing the impact of GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates on the currency pair. The Reserve Bank of Australia's monetary policy and the Bank of Canada's responses played pivotal roles in shaping the pair's movements. Additionally, the influence of China on the Australian economy and global trade tensions affecting the Canadian dollar underscored external factors influencing the exchange rate.
B. Overview of bullish or bearish stance based on analysis
The bullish or bearish stance was influenced by these factors. Divergent monetary policies led to interest rate differentials, impacting the AUDCAD exchange rate. Moreover, the AUD's sensitivity to China's economic performance and the CAD's susceptibility to trade tensions contributed to directional biases.
C. Final thoughts on trading the AUDCAD currency pair based on fundamental analysis and trading strategies
Ultimately, trading strategies for the AUDCAD pair centered on technical analysis, risk management, and news trading. Identifying trends, leveraging indicators, setting risk parameters, and capitalizing on news-driven volatility were all crucial components of effective trading strategies.
In conclusion, the AUDCAD currency pair demands a nuanced understanding of macroeconomic indicators and their implications, along with well-defined trading strategies. Success in trading this pair requires a harmonious integration of fundamental insights, technical tools, and risk management practices. Traders can navigate the complexities of this currency pair by continually refining their approach based on both fundamental analysis and effective trading strategies.

















