The fundamental analysis of the EURNZD currency pair involves evaluating the underlying factors influencing the exchange rate between the euro (EUR) and the New Zealand dollar (NZD). Fundamental analysis plays a vital role in predicting currency movements. By examining economic indicators such as GDP, inflation rates, interest rates, and employment data, traders can gain insights into the strength or weakness of a currency. This analysis helps identify trends, assess potential risks, and make informed trading decisions.
The EURNZD currency pair represents the exchange rate between the euro, the currency of the Eurozone, and the New Zealand dollar, the currency of New Zealand. It reflects the relative value of these two currencies and is influenced by various economic indicators, geopolitical events, and monetary policies.
The euro, abbreviated as EUR, is the common currency used by 19 European Union member states. It is managed by the European Central Bank (ECB) and is one of the most actively traded currencies globally. The New Zealand dollar, denoted as NZD, is the official currency of New Zealand. It is influenced by factors such as commodity prices, trade relationships, and the Reserve Bank of New Zealand's policies.
Macroeconomic Overview - Eurozone

Understanding the macroeconomic landscape, including GDP, unemployment, inflation rates, business and consumer confidence, monetary policies, and the impact of political events like Brexit, is essential in conducting a thorough fundamental analysis of the EURNZD currency pair. To analyze the fundamental factors influencing the EURNZD currency pair, let's review key economic indicators in the Eurozone.
A. Economic Indicators Review
The Eurozone experienced a challenging period in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic. However, it rebounded in 2021 and 2022, with GDP growth rates of 4.6% and 4.2%, respectively. After reaching a peak of 8.4% in 2020, the unemployment rate gradually decreased to 7.1% in 2022.

Besides, inflation in the Eurozone has been moderate but experienced some fluctuations. In 2020, it stood at 0.3%, below the European Central Bank's (ECB) target of close to 2%. However, in 2022, inflation increased to 2.1%, reflecting improved economic conditions.
Business and consumer confidence indicators are essential in assessing economic sentiment. Following the pandemic-induced slump, business and consumer confidence recovered steadily in 2021 and 2022, indicating growing optimism within the Eurozone.
B. Monetary Policy

The ECB's primary objective is to maintain price stability and support economic growth. In response to the pandemic, the ECB implemented expansionary monetary policies, including asset purchases and low-interest rates, to stimulate the economy. These measures were gradually adjusted as the economy recovered.
Moreover, interest rate expectations influence currency valuation. In recent years, the ECB has kept interest rates at historically low levels. However, as the Eurozone's economic recovery gains traction, there may be expectations for future interest rate hikes.
C. Political Climate

The economic policies of Eurozone governments play a crucial role in shaping the currency's performance. Policies focusing on fiscal stimulus, infrastructure investments, and structural reforms can impact economic growth and currency valuation.
Also, Brexit, the United Kingdom's departure from the European Union, has had economic consequences for both parties. While Brexit's initial uncertainties affected the euro and the Eurozone, subsequent trade agreements and economic adjustments have mitigated some negative effects.
Macroeconomic Overview - New Zealand
By considering key economic indicators, the monetary policy of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, and the impact of political factors and global trade disputes, you can gain valuable insights into the fundamental factors that influence the EURNZD currency pair.
This analysis allows you to make informed trading decisions based on a comprehensive understanding of the New Zealand economy. To conduct a comprehensive fundamental analysis of the EURNZD currency pair, it is important to review key economic indicators in New Zealand.
A. Economic Indicators Review
New Zealand's economy experienced a contraction in 2020 due to the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. However, it rebounded strongly in 2021 and 2022, with GDP growth rates of 3.1% and 3.9%, respectively. The unemployment rate peaked at 5.2% in 2020 and gradually declined to 4.3% in 2022. And inflation in New Zealand has been relatively moderate. In 2020, it stood at 1.4%, below the Reserve Bank of New Zealand's (RBNZ) target range of 1-3%. However, in 2022, inflation increased to 2.7%, reflecting a pickup in economic activity.
Business and consumer confidence are important indicators of economic sentiment. After a decline in 2020, both business and consumer confidence improved in 2021 and 2022, indicating a positive outlook for the New Zealand economy in 2023.
B. Monetary Policy

The RBNZ's primary objective is to maintain price stability and support sustainable economic growth. The RBNZ implemented accommodative monetary policies in response to the pandemic, including low-interest rates and quantitative easing measures. As the economy recovered, the central bank adjusted its policy stance accordingly.
Interest rate expectations can significantly impact currency valuations. The RBNZ has maintained historically low-interest rates to stimulate economic growth. However, as the New Zealand economy continues to recover, there may be expectations for future interest rate hikes.
C. Political Climate
The economic policies of the New Zealand government play a crucial role in shaping the country's economic performance. Policies focusing on infrastructure investments, employment growth, and sustainable development contribute to overall economic stability and investor confidence.
New Zealand's economy is heavily reliant on international trade. Global trade disputes, such as tariff conflicts or supply chain disruptions, can significantly impact the country's exports and economic growth. Monitoring these developments is crucial for assessing the potential effects on the New Zealand dollar.
Analysis of the EURNZD Currency Pair
To conduct a thorough fundamental analysis of the EURNZD currency pair, it is crucial to consider the correlation between the eurozone and New Zealand economies. Factors such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates also play a significant role in shaping the currency pair's dynamics.
A. Relevant Economic Indicators
While the eurozone represents a major economic bloc with diverse member countries, New Zealand is a smaller, export-oriented economy. However, global economic conditions and market sentiment can create correlations between the two economies, impacting the EUR/NZD currency pair.
GDP growth is a vital indicator of economic performance. Higher GDP growth rates in either the eurozone or New Zealand can positively influence their respective currencies. Inflation rates and interest rates also have an impact. Higher inflation rates may prompt central banks to raise interest rates, potentially strengthening their currencies.
B. Factors Supporting a Bullish or Bearish Stance

Several factors can influence whether a bullish or bearish stance is appropriate for the EUR NZD currency pair. The European Central Bank (ECB) is crucial in determining the eurozone's monetary policy. Policy decisions like interest rate adjustments, quantitative easing measures, and forward guidance can impact the euro. A hawkish stance (tightening monetary policy) may strengthen the euro, while a dovish stance (loosening policy) may weaken it.
Similarly, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) has the authority to set monetary policy in New Zealand. Interest rate decisions and other policy measures taken by the RBNZ can influence the New Zealand dollar. A hawkish RBNZ may strengthen the currency, while a dovish RBNZ may weaken it.
As both the eurozone and New Zealand rely heavily on international trade, global trade disputes can significantly affect their respective currencies. Tariffs, trade tensions, or disruptions to supply chains can lead to fluctuations in the EURNZD currency pair.
C. Potential Risks to the Currency Pair

When analyzing the EURNZD currency pair, it is important to consider potential risks impacting its performance. Unforeseen changes in global trade policies, such as the imposition of new tariffs or trade restrictions, can create volatility in currency markets, affecting the EURNZD exchange rate.
Unanticipated shifts in the monetary policies of the eurozone or New Zealand, driven by economic developments or unforeseen events, can lead to fluctuations in the respective currencies, impacting the EURNZD pair.
Natural disasters or geopolitical events can adversely affect the eurozone and New Zealand economies, potentially influencing the EURNZD currency pair. These events may disrupt trade, affect investor sentiment, or create economic instability.
Analyzing the relevant economic indicators, assessing factors supporting a bullish or bearish stance, and identifying potential risks will allow you to develop a more comprehensive understanding of the fundamental factors driving the EURNZD currency pair. This analysis empowers you to make informed trading decisions based on the dynamics of the eurozone and New Zealand economies.
Trading Strategies for EURNZD
When it comes to trading the EURNZD currency pair, a combination of fundamental and technical analysis can help you develop effective trading strategies. Here are some key approaches to consider:
A. Technical Analysis
The technical analysis evaluates financial markets and makes trading decisions based on price patterns, trends, and indicators rather than analyzing fundamental factors.
Analyzing price charts can help you identify trends, such as uptrends, downtrends, or sideways movements. Additionally, you can look for chart patterns like triangles, head and shoulders, or double tops/bottoms, which can provide insights into potential market reversals or continuation patterns.
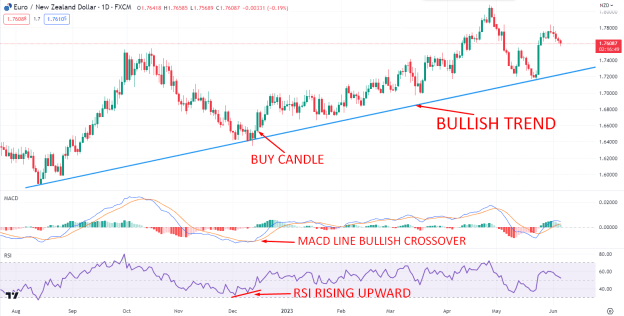
Also, technical indicators such as the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD) and Relative Strength Index (RSI) can provide additional confirmation signals. The MACD helps identify trend strength and potential crossovers, while the RSI indicates overbought or oversold conditions, aiding in timing entry or exit points.
B. Risk Management
Risk management is the process of identifying, assessing, and controlling potential risks in order to minimize losses and protect against adverse events. So, establishing predetermined levels for stop-loss and take-profit orders helps manage risk and protect your trading capital. Stop-loss orders are placed below the entry price to limit potential losses, while take-profit orders are set at a desired profit target to secure gains.

Position sizing should be based on your risk tolerance and the distance between your entry point and stop-loss level. By considering the percentage of your trading account you are willing to risk per trade, you can determine an appropriate position size that aligns with your risk management strategy.
C. News Trading
News trading is a trading strategy involving making decisions based on the immediate market impact of significant news events and economic data releases.
Stay updated on economic events and data releases that can impact the EURNZD currency pair. Key reports include GDP growth, inflation figures, central bank announcements, and trade data. These events often create market volatility and trading opportunities.
Monitor how the market reacts to news releases. If data deviates significantly from expectations, it can trigger sharp movements in the currency pair. Reacting swiftly to these market dynamics can lead to profitable trades.
When implementing these strategies, choosing a reliable and user-friendly trading platform like VSTAR is important. VSTAR provides a seamless trading experience, offering access to various currency pairs, including EURNZD. With VSTAR, you can enjoy fast execution, advanced charting tools, and comprehensive market analysis to support your trading decisions.
Remember to combine technical and fundamental analysis, practice risk management, and stay informed about economic events. Regularly review and adjust your trading strategies as market conditions evolve. By following these steps and leveraging the features of VSTAR, you can enhance your trading potential in the EURNZD currency pair.
Trade EURNZD on VSTAR today and seize trading opportunities with a fast, efficient, and user-friendly platform that works for you. Trade EURNZD on VSTAR today and take advantage of the tools and resources available to enhance your trading experience.
Conclusion
Fundamental analysis of the EURNZD currency pair, we examined the macroeconomic overview of both the eurozone and New Zealand. Based on the analysis, a bullish stance on the EURNZD currency pair may be supported by positive GDP growth in the eurozone, low inflation rates, and an accommodative monetary policy by the European Central Bank.
However, a bearish stance may be influenced by the impact of global trade disputes and any unexpected changes in monetary policies in either region.
When trading the EURNZD currency pair, it is essential to consider both fundamental and technical analysis. You can make more informed trading decisions by combining an understanding of economic factors with technical indicators and risk management strategies.




