I. Introduction
A. Overview of the AUD/NZD currency pair
The AUD/NZD currency pair represents the exchange rate between the Australian dollar (AUD) and the New Zealand dollar (NZD). This pair is crucial in the forex market due to the economic ties and geographical proximity between Australia and New Zealand. Fundamental analysis is pivotal in comprehending the dynamics of this currency pair, as it involves evaluating economic indicators, fiscal policies, and geopolitical events that impact the value of the AUD and NZD.
B. Importance of fundamental analysis
Understanding the fundamental factors influencing the Australian and New Zealand dollars is critical to predicting the direction of this currency pair. The interaction between these two currencies hinges on various factors. One significant influence is the trade relationship between Australia and New Zealand. Being key trading partners, changes in their trade dynamics can impact the AUD NZD pair. Moreover, interest rate differentials and commodity prices have a significant impact on their respective currencies. A higher interest rate in one country can attract more foreign investment, thus strengthening its currency.
Geopolitical events also have a role to play. Political stability, economic reforms, and global events can lead to fluctuations in the AUD/NZD exchange rate. For instance, shifts in China's demand for commodities can affect both the Australian and New Zealand economies, given their export-oriented markets.

C. A brief explanation of the Australian dollar and New Zealand dollar
The Australian dollar, AUD, is the currency of Australia and is influenced by factors such as the country's GDP growth, employment rates, interest rates, and commodity prices, especially those of iron ore and coal.
The New Zealand dollar, NZD, serves as the official currency of New Zealand. It is subject to comparable determinants, including New Zealand's GDP growth, dairy and agricultural product prices, interest rates, and trade relationships.
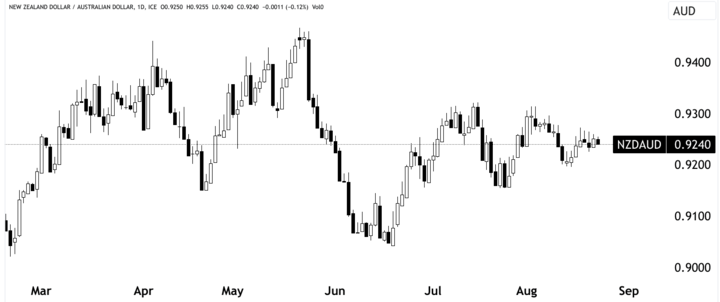
Source: tradingview.com
II. Macroeconomic Overview: Australia
A. Economic Indicators Review
1. GDP and Unemployment Rate
Australia's economic performance greatly influences the AUD NZD currency pair. As of August 2023, Australia's GDP growth rate was approximately 2.3%.
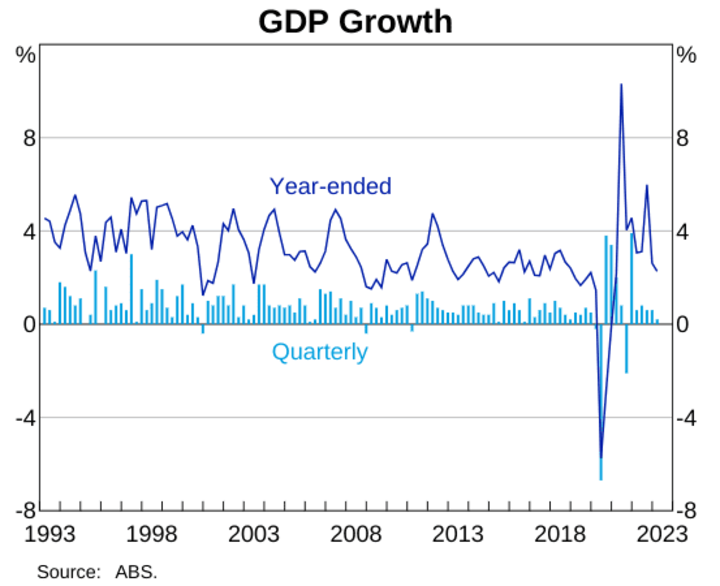
Source: rba.gov.au
This relatively modest growth was partly attributed to the disruptions caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and global macro adversities. Concurrently, the unemployment rate stood at 3.7%, reflecting labor market stability despite pandemic-induced challenges. These figures showcased the country's resilience in the face of economic headwinds.
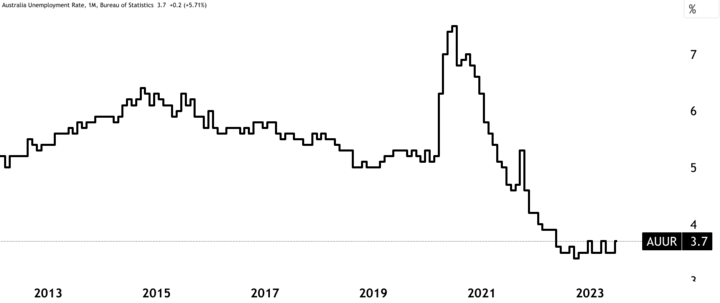
Source: tradingview.com
2. Inflation Rates
Inflation is a key factor impacting currency value. Australia's inflation rate is currently relatively high, with consumer prices rising by around 6% annually. The Reserve Bank of Australia (RBA) closely monitored inflation trends to guide its monetary policy decisions.
3. Business and consumer confidence
Both business and consumer confidence indicators are crucial for understanding economic sentiment. During this period, Australian businesses displayed cautious optimism, with business confidence at moderate levels. Consumer sentiment, influenced by factors such as employment prospects and economic stability, played a role in shaping domestic consumption trends.

Source: tradingview.com
B. Monetary Policy
1. The Reserve Bank of Australia's Monetary Policy
The RBA's monetary policy decisions significantly impacted the AUD's value. The central bank had maintained historically high-interest rates, at around 4.1%, to cage inflation amid the pandemic's aftermath. These measures aimed to encourage borrowing and spending, which in turn influenced economic growth and inflation.
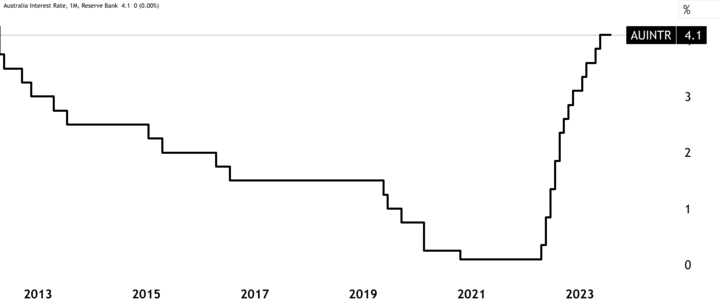
Source: tradingview.com
2. Interest Rate Expectations
Anticipating changes in interest rates is vital for currency traders. Interest rate differentials between Australia and New Zealand can affect the AUD/NZD exchange rate. Investors closely followed the RBA's statements and actions to predict potential shifts in interest rates. Any indications of future rate hikes or cuts could lead to speculative movements in the currency pair.
C. Political Climate
1. Economic policies of the government
Australia's political landscape plays a role in shaping economic policies that impact the currency. The government's fiscal decisions, including budget allocations and stimulus packages, contribute to economic growth. During this period, the Australian government introduced measures to support industries affected by the pandemic, emphasizing the importance of fiscal policy in economic recovery.
2. Impact of China on the Australian economy
China's influence on Australia's economy is notable due to trade relationships and demand for commodities. China is a major trading partner for Australia, particularly in terms of exports like iron ore and coal. Economic developments in China, such as changes in demand for these commodities or geopolitical tensions, can have cascading effects on Australia's economy and subsequently influence the AUD/NZD currency pair.
III. Macroeconomic Overview: New Zealand
A. Economic Indicators Review
1. GDP and Unemployment Rate
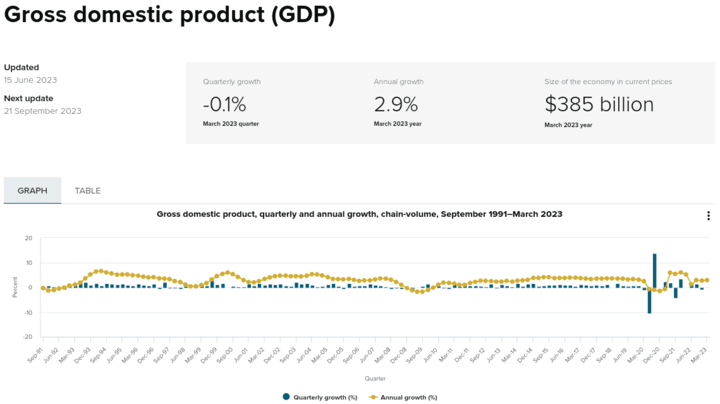
Source: stats.govt.nz
New Zealand's economic performance is a key driver of the AUD/NZD currency pair. As of the March quarter of 2023, New Zealand's GDP growth rate was around 2.9%. This relatively modest growth was partly attributed to the global economic uncertainties caused by the ongoing pandemic. Concurrently, the unemployment rate stood at 3.6% (June 2023), reflecting New Zealand's relatively stable labor market despite the challenges posed by the pandemic.

Source: stats.govt.nz
2. Inflation Rates
Inflation plays a crucial role in shaping a country's monetary policy and currency value. New Zealand is currently experiencing high inflation, with consumer prices rising by approximately 6.0% annually. The Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) closely monitored inflation trends to ensure price stability and to guide its monetary policy decisions.
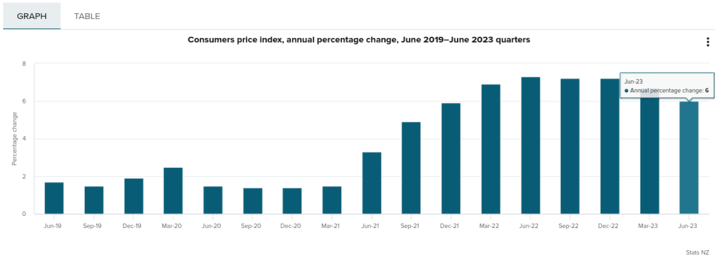
Source: stats.govt.nz
3. Business and consumer confidence
Business and consumer sentiment are pivotal indicators of economic health. New Zealand's businesses exhibited cautious optimism during this period, with business confidence reflecting the ongoing impact of global uncertainties on trade and investment. Consumer sentiment, influenced by factors like employment outlook and purchasing power, contributed to shaping domestic consumption patterns.
B. Monetary Policy
1. The Reserve Bank of New Zealand's Monetary Policy
The RBNZ's monetary policy decisions had a significant impact on the New Zealand dollar's value. The central bank maintained an interest rate of approximately 5.5% during this time to address inflationary pressures. Like other central banks, the RBNZ employed these measures to encourage borrowing, spending, and investment, aiming to stimulate economic growth and maintain price stability.
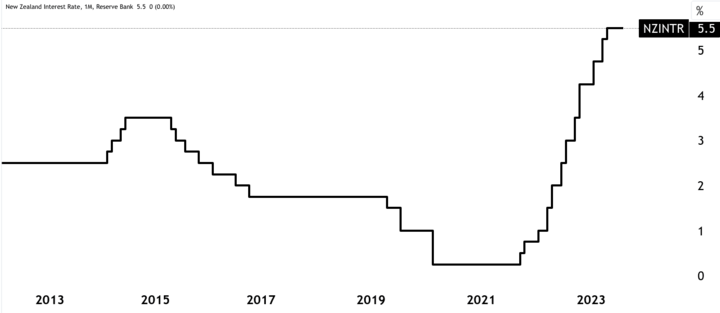
Source: tradingview.com
2. Interest Rate Expectations
Anticipating changes in interest rates is pivotal for currency traders. The difference in interest rates between New Zealand and Australia can impact the AUD/NZD exchange rate. Investors closely followed the RBNZ's statements and actions to predict potential shifts in interest rates. Any indication of future rate adjustments could trigger speculative movements in the currency pair.
C. Political Climate
1. Economic policies of the government
New Zealand's political landscape plays a role in shaping economic policies that influence the currency. The government's fiscal decisions, including budget allocations and stimulus measures, impact economic growth and recovery. During this period, the New Zealand government introduced initiatives to support sectors affected by the pandemic, highlighting the importance of fiscal policy in economic stabilization.
2. Impact of global trade tensions on the New Zealand economy
New Zealand's economy is highly dependent on international trade, making it susceptible to global trade tensions. Changes in international trade agreements or disruptions in supply chains can impact the country's exports and imports. Any shifts in demand for New Zealand's key exports, such as agricultural products, can influence the country's economic outlook and consequently affect the AUDNZD currency pair.
IV. Analysis of the AUD NZD Currency Pair
A. Relevant Economic Indicators
1. Correlation between the Australian and New Zealand economies
The AUD/NZD currency pair's dynamics are deeply influenced by the economic ties between Australia and New Zealand. Given their geographic proximity and trade relationships, the two economies often move in tandem. This correlation is significant for traders and investors as it informs them about potential joint movements in the currency pair.
2. Impact of GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates on the currency pair
GDP growth, inflation rates, and interest rates are fundamental indicators that wield substantial influence over the AUD NZD currency pair.
- Strong GDP growth in Australia could indicate robust economic activity and potentially lead to an appreciation of the Australian dollar, impacting the currency pair. Similarly, New Zealand's GDP growth can impact the NZD's value.
- High inflation rates may lead to central banks raising interest rates to curb price increases. This can attract foreign investment and strengthen the respective currency. Conversely, low inflation rates could prompt central banks to adopt accommodative policies, potentially weakening the currency.
- Interest rate differentials between Australia and New Zealand can significantly impact the currency pair. If one country's central bank raises interest rates while the other maintains low rates, it can lead to a shift in investor sentiment and consequently affect the exchange rate.
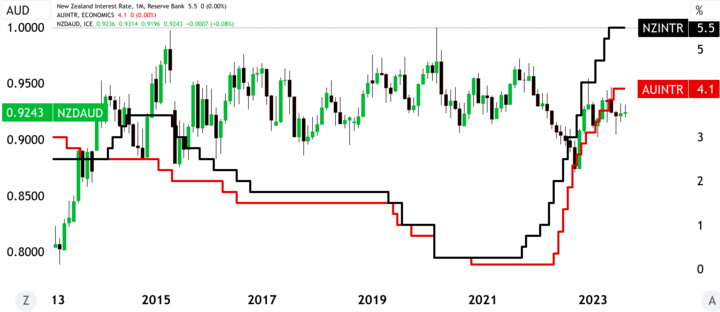
Source: tradingview.com
B. Factors Supporting a Bullish or Bearish Stance
1. Impact of the Reserve Bank of Australia's monetary policy on the currency pair
The Reserve Bank of Australia's (RBA) monetary policy decisions play a pivotal role in shaping the AUD's value. If the RBA raises interest rates or adopts a hawkish stance due to strong economic indicators, it could attract foreign capital and strengthen the Australian dollar, potentially resulting in a bullish outlook for the AUD/NZD currency pair.
2. Impact of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand's monetary policy on the currency pair
Similarly, the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) significantly impacts the NZD's value through its monetary policy. If the RBNZ tightens monetary policy due to inflation concerns, this may lead to a bullish stance for the NZD. Conversely, a dovish stance aimed at stimulating the economy could result in a bearish outlook for the AUD NZD pair.
3. Impact of China on the Australian economy and global trade tensions on the New Zealand economy
China's role as a major trading partner for both Australia and New Zealand is a significant determinant of the AUD/NZD currency pair. Any shifts in China's demand for commodities, especially from Australia, can affect both economies. Moreover, global trade tensions can disrupt New Zealand's export-oriented economy, potentially influencing the currency pair's direction.
C. Potential Risks to the Currency Pair
1. Sudden changes in global economic growth
A sudden slowdown in global economic growth, as witnessed during the COVID-19 pandemic, can disrupt trade flows and impact both the Australian and New Zealand economies. This could lead to unexpected movements in the AUD/NZD currency pair as traders reassess their economic outlooks.
2. Unpredicted changes in Australian or New Zealand monetary policies
Central banks' decisions are closely watched by traders. Any unanticipated shifts in monetary policies, whether due to economic surprises or changes in global conditions, can lead to swift and significant movements in the AUD NZD exchange rate.
3. Geopolitical risks, such as trade tensions between the U.S. and China
Geopolitical events, such as trade tensions between major economies like the U.S. and China, can have cascading effects on global trade and economic sentiment. These events can trigger risk aversion, impacting commodity prices, trade relationships, and currency values, potentially affecting the AUDNZD currency pair.
V. Trading Strategies for AUD NZD
A. Technical Analysis
1. Identifying trends and patterns
Technical analysis involves studying historical price data to predict future price movements. Traders often analyze trends and chart patterns in the AUD NZD currency pair. Trends, whether upward (bullish) or downward (bearish), can help traders determine the prevailing direction. Chart patterns, such as head and shoulders, double tops, and triangles, provide insights into potential reversals or continuations of trends.

Source: tradingview.com
2. Use of indicators such as moving averages and Fibonacci retracements
Technical indicators aid traders in making informed decisions. Moving averages, for instance, help smooth out price data to identify trends more clearly. Traders may also employ Fibonacci retracements to pinpoint potential support and resistance levels. These tools assist in timing entry and exit points for trades.
B. Risk Management
1. Setting stop-loss and take-profit levels
Risk management is an integral part of successful trading. Traders often use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses on a trade if the market moves against them. Take-profit orders are used to lock in profits when the trade moves in their favor. Properly placing these levels requires analysis of historical price movements and volatility.
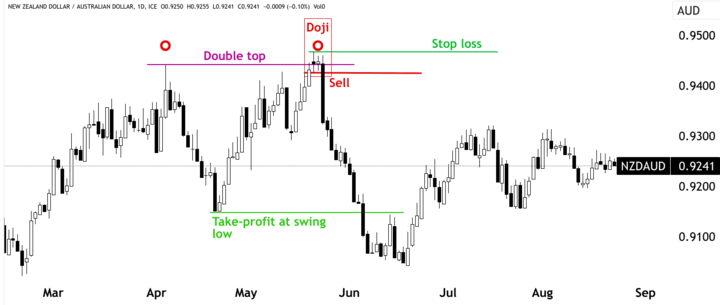
Source: tradingview.com
2. Determining position size based on risk tolerance
Position sizing is essential for risk management and capital preservation. Traders calculate position sizes based on their risk tolerance and the distance between the entry point and the stop-loss level. This ensures that a single trade doesn't excessively impact their overall trading capital.
C. News Trading
1. Following economic events and data releases
News trading involves capitalizing on market reactions to economic events and data releases. Traders monitor economic calendars for key indicators like GDP growth, employment figures, and interest rate decisions. In the case of AUD NZD, traders would pay attention to both Australian and New Zealand economic indicators.
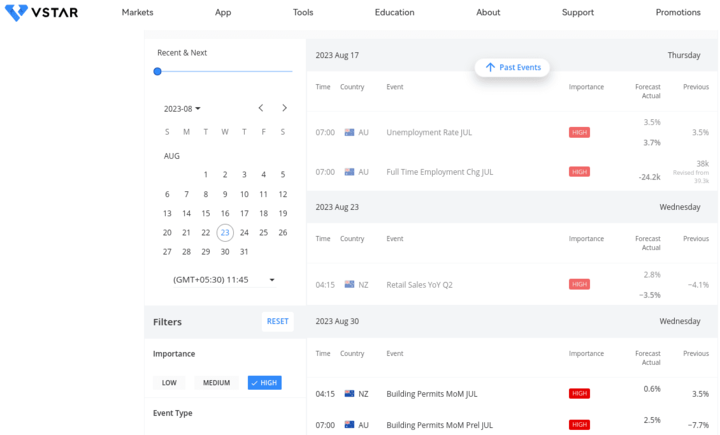
Source: vstar.com
2. Trading based on market reactions to news
Once specific news is released, the market can exhibit high volatility. Traders often employ different strategies based on the news outcome:
- Directional Trades: If the released data significantly deviates from expectations, traders might place trades in the direction of the market's reaction. For example, positive economic data for Australia could lead to a bullish stance on the AUD NZD pair.
- Reversal Trades: Sometimes, news releases can lead to short-lived market movements. Traders may use this opportunity to enter trades against the initial reaction, expecting a reversal as the market digests the news.
VI. Trade AUD NZD with VSTAR
VSTAR offers compelling reasons to trade forex, making it an attractive choice for both novice and experienced traders.
Competitive Leverage:
With leverage of up to 1:200, VSTAR enables traders to amplify their trading power. This allows for more trading opportunities even with smaller capital, potentially leading to increased profits. For example, with $1,000 in capital and 1:200 leverage, traders can control positions worth $200,000.
Top-tier deep liquidity:
VSTAR provides traders with access to top-tier deep liquidity, facilitating the swift execution of trades. This ensures that traders can enter and exit positions promptly, capturing market opportunities in real-time.
Spreads from 0 pips:
VSTAR offers traders a competitive edge with spreads starting at 0 pips on major products. Tight spreads reduce trading costs, allowing traders to maximize potential profits.
Best Execution:
VSTAR guarantees the best execution for traders. Orders are filled at the best available market prices, ensuring that traders receive favorable entry and exit points. The lightning-fast execution, within milliseconds, minimizes slippage and ensures that traders' intentions are accurately executed.
Incorporating competitive leverage, deep liquidity, tight spreads, and exceptional execution, VSTAR creates an environment conducive to effective forex trading. These factors enhance traders' ability to capitalize on market movements and achieve their trading goals.
VII. Conclusion
A. Recap of the fundamental analysis of the AUD/NZD currency pair
In assessing the AUDNZD currency pair, fundamental analysis has been pivotal. Economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, inflation, and interest rates were scrutinized for both Australia and New Zealand. The monetary policies of the Reserve Bank of Australia and the Reserve Bank of New Zealand, along with the influence of China on the Australian economy and global trade tensions in New Zealand, were integral to understanding the pair's dynamics.
B. Overview of bullish or bearish stance based on analysis
Based on the analysis, a bullish or bearish stance can be contingent on various factors. Strong GDP growth and favorable economic conditions in Australia, coupled with hawkish RBA policies, could suggest a bullish outlook for the AUD. Conversely, an easing RBNZ policy in New Zealand, along with subdued economic growth, might indicate a bearish stance for the NZD. Furthermore, the influence of China's demand for commodities and global trade tensions can sway the pair's trajectory.
C. Final thoughts on trading the AUD/NZD currency pair based on fundamental analysis and trading strategies
Incorporating fundamental analysis into trading strategies for the AUD NZD currency pair is essential. Traders should be attuned to economic indicators, central bank policies, and geopolitical events that can impact the pair's performance. Technical analysis, risk management, and news trading strategies should be applied judiciously to leverage potential market opportunities and mitigate risks.




