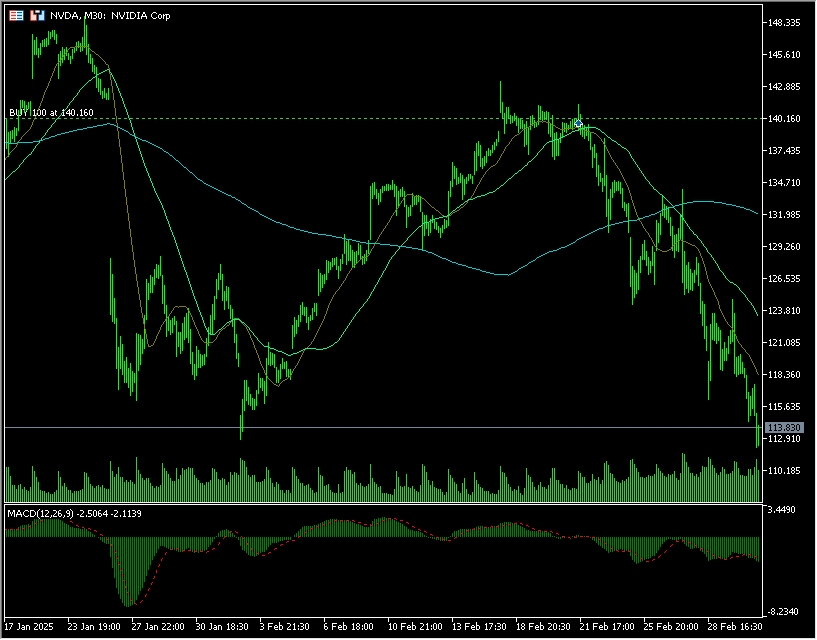
Last night, large-cap technology stocks in the U.S. stock market fell across the board, with Nvidia falling 8.69% and falling 10% during the session. Although its revenue in fiscal year 2025 hit a record high, its stock price fluctuated after the release of the financial report due to the evaporation of nearly 2 trillion yuan in market value in a single day. However, Bank of America said that Nvidia is still a reliable investment and raised its target price by 5%. The bank reiterated its "buy" rating on Nvidia and raised its year-end target share price from $190 to $200, which means that the stock can rise by more than 60% from the current level. Behind this optimistic expectation, there are both Nvidia's core advantages in the field of AI and the need to face the intensified competition and the divergence of market sentiment.

High performance growth and the certainty of AI leadership
Explosive growth in revenue and profits
Nvidia's full-year revenue for fiscal year 2025 reached US$130.5 billion (approximately RMB 947.4 billion), a year-on-year increase of 114%, and net profit of US$72.88 billion, a year-on-year increase of 145%. Among them, the data center business revenue in the fourth quarter was US$35.6 billion, accounting for more than 90% of the total revenue, a year-on-year increase of 93%. This growth mainly benefited from the outbreak of generative AI and the continued investment of cloud vendors in computing power. CEO Huang Renxun emphasized that the demand for the AI reasoning market is still in the "early stages", and the popularization of multimodal and enterprise-level AI in the future will drive a new round of growth.
Blackwell chip's technical barriers
Nvidia's next-generation Blackwell chip has entered the mass production stage, and its performance is regarded by the industry as the key to consolidating its leadership in the AI chip market. The chip not only improves computing efficiency, but also builds a full-stack solution through Spectrum-X Ethernet technology and AI software ecology, becoming the core driving force for data center upgrades. Although Blackwell's delivery progress has caused market concerns, its shortage is still regarded by institutions as a guarantee for future growth.
Bank of America's bullish logic: demand expansion and ecological moat
Long-term demand for AI computing power
Bank of America and other institutions believe that the transformation of AI from training to inference will give rise to a wider demand for computing power. Nvidia's GPU is not only the "infrastructure" for training large models, but its CUDA software ecology and developer community are barriers that are difficult to replicate. Huang Renxun pointed out that generative AI will "completely change every industry", and Nvidia's full-stack platform covers the entire chain from chips to applications. This ecological advantage may support its pricing power.
Incremental space in emerging markets
In addition to data centers, Nvidia's layout in the fields of automobiles, robots, AI glasses, etc. has opened up new growth points for it. For example, the autonomous driving chip in cooperation with Toyota, the launch of Project Digits personal AI supercomputer, and the application of AR glasses patents all show the potential for diversified business. Research institutions predict that the penetration rate of AI glasses may reach 20% by 2030, and Nvidia's technology reserves are expected to take the lead in this track.
Risks and challenges: hidden worries under high expectations
Competitive pressure and shrinking gross profit margins
Although Nvidia dominates the AI chip market, the catch-up of traditional manufacturers such as AMD and Intel, as well as the trend of self-developed chips by Google and Microsoft, are diverting some orders. What is more noteworthy is that the low-cost open source inference model R1 launched by Chinese startup DeepSeek directly impacted the market's demand expectations for Nvidia GPUs, causing its stock price to plummet 17% in a single day. In addition, Nvidia's gross profit margin has fallen from its peak to around 70%. If it shrinks further in the future, it may weaken its profit elasticity.
Valuation overdraft and market sentiment fluctuations
At present, Nvidia's price-to-sales ratio (P/S) is about 31 times, higher than competitors such as Broadcom. Some analysts believe that its stock price has reflected growth expectations for many years to come. The influx of retail investors (net purchases of $29.8 billion in 2024) has pushed up the stock price, but it has also increased volatility. For example, after the CES conference in January 2025, the stock price fell by more than 6% in a single day due to the lack of short-term positive details.
Conclusion: Balance between short-term volatility and long-term potential
Bank of America's increase in Nvidia's target price is essentially a recognition of the long-term value of its AI ecosystem. However, investors need to be wary of two contradictions:
Technology leadership and market saturation: Can Nvidia replicate its dominance in the training stage in the inference market?
High growth and cyclical risks: The strong cyclicality of the semiconductor industry may expose valuation bubbles when demand slows in the future.
Overall, if Nvidia's stock price is to achieve a 60% increase, it needs to rely on the continued expansion of Blackwell chips, commercial breakthroughs in emerging businesses, and further expansion of global AI capital expenditures. Short-term fluctuations may be difficult to avoid, but in the long run, Nvidia is still one of the most certain "shovel" targets in the AI wave.
*Disclaimer: The content of this article is for learning only, does not represent the official position of VSTAR, and cannot be used as investment advice.