I. Introduction
Explanation of Gold CFDs and the US Dollar
Gold CFDs (contracts for difference) are derivative instruments to speculate on the price of gold movements without owning the physical commodity. Instead, a CFD is a contract between the trader and the CFD provider that enables the trader to profit from changes in the gold price without taking physical delivery of the asset. The trader earns a profit or loss based on the range between the open and close prices of the CFD.
The US Dollar is the most significantly traded currency in the world and is often used as the currency of choice for trading Gold CFDs. It is because gold is priced in US Dollars, and changes in the value of the US Dollar can significantly impact the price of gold. Several factors can affect the value of the US Dollar and, in turn, the price of Gold CFDs. One of the most significant is monetary policy. The US Federal Reserve can influence the value of the US Dollar by updating its monetary policy decisions, such as changes to interest rates or the money in circulation.
A summary of the correlation between Gold CFDs and the US Dollar
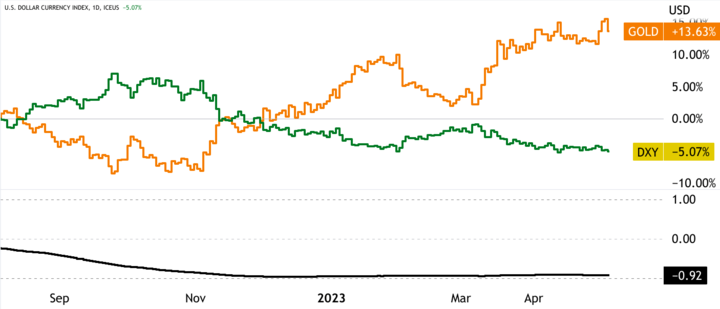
Gold CFDs and the US Dollar have a complex and often inverse relationship based on several economic and geopolitical factors. Gold is priced in US Dollars, which means that any fluctuations in the value of the US Dollar can impact the price of gold and, in turn, the value of Gold CFDs.
When the value of the US Dollar increases, the price of gold usually decreases, and vice versa. It is because when the US Dollar is more robust, it takes fewer US Dollars to buy an ounce of gold, making gold relatively cheaper and less attractive as an investment. Conversely, when the US Dollar is weaker, it requires more US Dollars to buy an ounce of gold, making gold relatively more expensive and more attractive as an investment.
It's also important to note that the correlation between Gold CFDs and the US Dollar is not always consistent or predictable. Other factors, such as changes in supply and demand for gold, can impact the Gold CFDs' price, even if the US Dollar is stable.
II. Understanding Gold CFDs
An explanation of what a CFD is
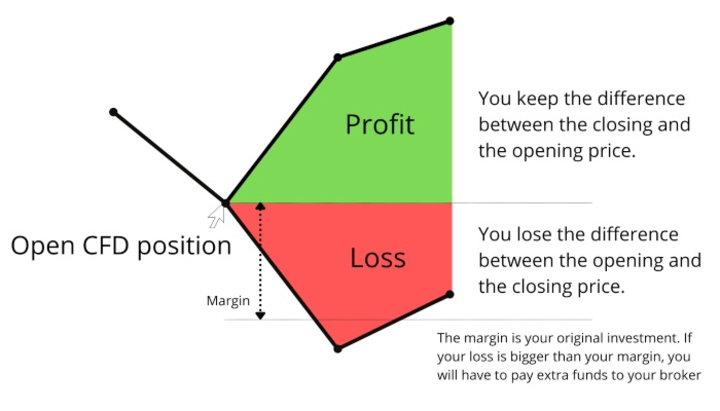
A CFD is a financial derivative to speculate and trade on the price movements of an underlying asset without owning the asset itself. When trading CFDs, the trader establishes a contract with a CFD provider, which enables them to profit from the difference between the open and close price of the CFD.
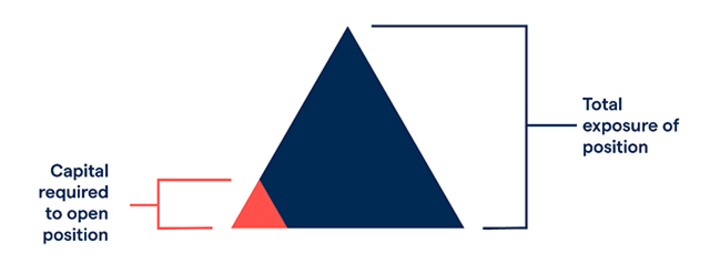
CFDs facilitate trading in various financial instruments, including stocks, commodities, currencies, and indices. CFDs are typically traded on margin, with only the need to deposit a fraction of the total value of the position to open a trade. It can allow traders to control a more significant position than the available capital.
How do Gold CFDs work?
Gold CFDs are instruments to speculate and trade on the price of gold movements without owning the physical asset itself. When trading Gold CFDs, the trader enters into a contract with a CFD provider that enables them to profit from the difference between the opening and closing price of the Gold CFD.
The Gold CFDs' price is closely tied to the price of physical gold in the market. However, Gold CFDs can be traded with greater flexibility and at lower costs than physical gold, making them a popular alternative for investors seeking exposure to the gold market.
When trading Gold CFDs, the trader can take either a long or short position on the price of gold. If the trader believes that the price of gold will rise, they can enter a long Gold CFD position. Conversely, if the trader believes that the price of gold will fall, they can enter a short Gold CFD position.
Advantages and disadvantages of Gold CFDs
Gold CFDs, or contracts for differences in gold, offer several advantages and disadvantages for traders seeking exposure to the gold market. Here are a few of the core advantages and disadvantages of trading Gold CFDs.
Advantages:
Flexibility: Gold CFDs offer traders greater flexibility than physical gold, as they can be traded at any time during trading hours, allowing traders to react quickly to changes in the market.
Lower costs: Gold CFDs can be traded at lower prices than physical gold, as there are no storage or delivery costs associated with CFD trading. It can make Gold CFDs a more cost-effective way to engage in exposure to the gold market.
Leverage: Gold CFDs allow traders to use leverage, which means they can control a more significant position than the available capital. It can magnify profitability, but it can also magnify potential losses.
Short selling: Gold CFDs allow traders to take a short position on the price of gold, enabling them to profit from a declining market.
Diversification: Gold CFDs provide traders with an additional tool for diversification in their portfolio, which can help manage risk.
Disadvantages:
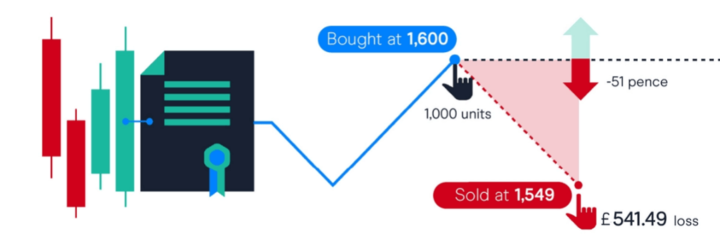
Risk: Trading Gold CFDs carries significant risk, and traders must carefully manage their risk exposure to avoid substantial losses. It's important to understand that losses can exceed deposits.
Counterparty risk: Gold CFDs are traded through a CFD provider, which exposes traders to counterparty risk. It means that if the CFD provider goes bankrupt, the trader's funds may be at risk.
Limited market hours: Gold CFDs can only be traded during market hours, which may limit the ability of traders to take advantage of price movements outside of trading hours.
Complexity: Gold CFDs can be complex instruments, and traders must have a good comprehension of the product before trading.
Lack of ownership: Gold CFDs do not provide traders with ownership of physical gold, which may not be suitable for those seeking to hold gold as a long-term investment or for those seeking a safe-haven asset during economic uncertainty.
III. Understanding the US Dollar
Explanation of the US Dollar and its Significance in international trade
The US Dollar (USD) is the world's most widely used currency in international trade, and its importance stems from several factors. The following element signifies the significance of the US Dollar in international trade.
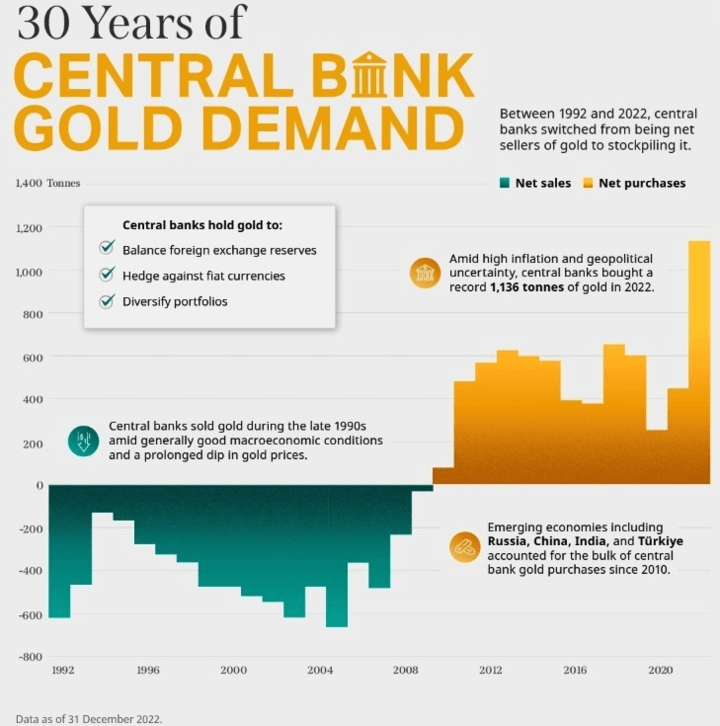
Reserve currency: The US Dollar is the world's primary reserve currency, which means that many central banks around the globe hold US Dollar reserves to hedge against inflation and facilitate international trade. As of 2021, the US Dollar accounted for around 60% of global foreign exchange reserves.
PetroUS Dollar system: The US Dollar has been a critical currency in the global oil trade since the 1970s when the US negotiated with Saudi Arabia to price oil in US Dollar. It has led to the widespread use of the US Dollar in the global energy markets and has helped to support the US Dollar's status as a dominant currency in international trade.

Safe-haven currency: The US Dollar is often considered a haven currency, as it is seen as a stable and reliable currency during times of global economic uncertainty. It has led to increased demand for the US Dollar during times of crisis, which has helped to maintain its value and importance in international trade.
Network effect: A network effect also reinforces the US Dollar's importance in international trade. The more widely a currency is used in international trade, the more attractive it becomes to use it for future transactions. It has helped to maintain the US Dollar's dominant position in international trade.
The significance of the US Dollar in international trade can be seen in several examples:
Commodity trade: Many commodity contracts, including oil, gold, and agricultural products, are priced in US Dollars. It means that countries that want to import these commodities need to hold US Dollars to pay for them, which increases demand for the US Dollar in global markets.
Foreign exchange markets: The US Dollar is the most actively traded currency in the foreign exchange markets, accounting for around 88% of daily forex turnover. It reflects the widespread use of the US Dollar in international trade and its importance in global financial markets.
Cross-border transactions: The US Dollar is often used as an intermediary currency for cross-border transactions between countries that do not have a direct currency exchange. For example, a transaction between a Brazilian and a Chinese company might be denominated in US Dollars, even though neither party is US-based.
Factors that impact the value of the US Dollar
The value of the US Dollar is impacted by various factors that affect the demand and supply of the currency. These factors can be broadly categorized into economic, political, and market-related factors. Here are a few critical factors that impact the value of the US Dollar.
Economic factors: Some critical economic factors that influence the value of the US Dollar include interest rates, inflation, economic growth, and the balance of trade. For example, if the US Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it could attract more foreign investors seeking higher returns, increasing demand for the US Dollar and pushing up its value.
Political factors: Political factors can also impact the value of the US Dollar. For example, political instability, geopolitical tensions, and policy changes by the US government can all affect the currency's value. For instance, uncertainty surrounding the US presidential elections or policy decisions such as tax reforms can create volatility in the US dollar's value.
Market-related factors: Factors such as supply and demand for the US Dollar in the foreign exchange market can also influence its value. The volume of international trade and capital flows primarily determines the demand for the US Dollar. If global demand for US exports increases, it can lead to a higher need for the US Dollar and a subsequent appreciation in its value.
Market sentiment: Market sentiment, or the overall mood of investors and traders, can also impact the value of the US Dollar. For example, if there is a perception of high risk or uncertainty in the global markets, investors may flock to safe-haven currencies such as the US Dollar, driving up its value. Conversely, if market sentiment turns hostile towards the US Dollar, it could lead to a decline in its value.
Monetary policy decisions: Decisions by central banks, such as the US Federal Reserve, regarding monetary policy, can have a considerable impact on the value of the US Dollar. For instance, if the Fed announces an increase in the money supply, it can lead to a reduction in the value of the US Dollar.
Overall, the value of the US Dollar is impacted by various factors, including economic, political, market-related, market sentiment, and monetary policy decisions. These factors are often interrelated, and changes in one element can generate a ripple effect on the others, leading to significant fluctuations in the currency's value. Investors and traders need to stay abreast of these factors to make informed decisions about buying and selling the US Dollar in the foreign exchange market.
IV. The Correlation Between Gold CFDs and the US Dollar
Historical analysis of the relationship between Gold CFDs and the US Dollar
The relationship between Gold CFDs and the US Dollar has been the subject of much analysis, given their importance in the global markets. Gold and the US Dollar have historically had an inverse relationship, meaning that as the value of the US Dollar strengthens, the price of gold tends to decline, and vice versa. The inverse relationship has been observed across various periods and market conditions, although the strength and consistency of the correlation have varied.
One example of the inverse relationship can be seen during the 1970s and early 1980s when the US Dollar experienced a decline. During that time, the price of gold enhanced dramatically as investors sought to hedge against inflation and the declining value of the US Dollar. Similarly, during the crisis of 2008–2009, the value of the US Dollar rose sharply as investors fled to safe-haven assets, leading to a decline in the price of gold.
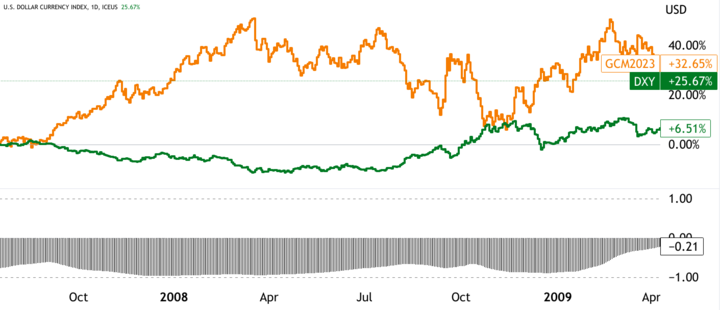
However, the relationship between gold and the US Dollar is not always straightforward. For example, during the period of quantitative easing in the aftermath of the 2008's financial crisis, the value of the US Dollar declined. Still, the price of gold did not rise as expected. It was due to various factors, including increased demand for gold in emerging markets, geopolitical tensions, and supply disruptions.
Furthermore, there have been periods where the correlation between gold and the US Dollar has broken down entirely, leading to divergent price movements. For example, from 2000 to 2008, gold and the US Dollar rose in value despite the historical inverse relationship between the two assets. It was due to a combination of geopolitical tensions, global economic growth, and rising demand for commodities.
How fluctuations in the US Dollar impact the value of Gold CFDs
Fluctuations in the US Dollar can significantly affect the Gold CFDs' worth, as these two assets are closely interrelated. How changes in the US Dollar can affect the value of Gold CFDs can be comprehended with examples of how these dynamics have worked out in the past.
Pricing Dynamics: One of the primary ways fluctuations in the US Dollar impact the value of Gold CFDs is through pricing dynamics. Gold is priced in US Dollars, which means that changes in the US Dollar value directly affect the price of gold. When the US Dollar strengthens, it takes fewer US Dollars to acquire the same quantity of gold, which can lead to a decrease in gold prices. Conversely, when the US Dollar weakens, it takes more US Dollars to acquire the same quantity of gold, which can lead to an increase in gold prices.
For instance, during the 2007-08 financial crisis, the US Dollar strengthened significantly as investors sought out safe-haven assets. It led to a sharp decrease in the price of gold, as the stronger US Dollar made it more expensive for investors outside the US to buy gold.
Currency Risk: Another way fluctuations in the US Dollar impact the value of Gold CFDs is through currency risk. If an investor buys Gold CFDs in a currency other than the US Dollar, fluctuations in the value of that currency can impact the investor's returns. For example, suppose an investor buys Gold CFDs denominated in euros, and the US Dollar strengthens relative to the Euro. In that case, the investor may see a decrease in the value of their investment, even if the price of gold stays at the same level.
Safe-Haven Dynamics: Finally, fluctuations in the US Dollar can impact the value of Gold CFDs through safe-haven dynamics. The US Dollar and gold are often seen as safe-haven assets, meaning that investors tend to buy them during economic uncertainty or market turmoil. If the US Dollar strengthens during such times, investors may shift their investments out of gold and into the US Dollar, which can lead to a reduction in the price of gold.
For example, during the COVID-19 pandemic, the US Dollar strengthened significantly as investors sought out safe-haven assets. It led to a decrease in the price of gold as investors shifted their investments away from gold and into the US Dollar.
The relationship between inflation rates and Gold CFDs
The relationship is complex, and several factors can impact the value of gold in an inflationary environment.
In general, gold can be considered a hedge against inflation, as its value tends to enhance in times of rising prices and currency devaluation. It is because gold is a tangible asset that is not tied to any specific currency and, therefore, can provide a store of value in times of economic uncertainty. As a result, investors often turn to Gold CFDs to protect their portfolios from inflationary pressures.
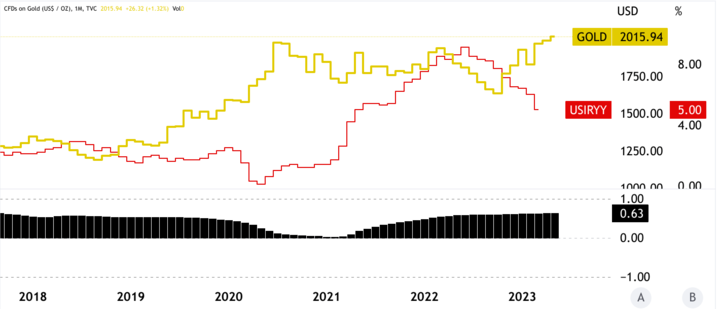
One instance of the relationship can be seen in the ongoing high inflation in the US. As inflation rates rose sharply, the value of the US Dollar declined, and the price of gold increased significantly. It led to a massive boost in gold demand as investors sought to protect their wealth from the eroding effects of inflation.
Notably, the relationship between inflation rates and Gold CFDs is not always direct. Other elements, such as geopolitical and economic adversities, supply-demand, and central bank policies, can also impact the price of gold. For example, during the period of quantitative easing by central banks in the aftermath of the financial crisis, the US dollar's value declined. Still, the price of gold did not rise as expected due to increased demand from emerging markets and geopolitical tensions.
In addition, inflation rates can vary depending on the country or region in question, and different factors may impact the Gold CFDs' value in other contexts. For example, Gold CFDs may be considered a safer investment option in countries with high inflation rates and unstable currencies. In contrast, other investments may be more attractive in countries with more stable economic conditions.
V. How to Trade Gold CFDs in a US Dollar Market
Strategies for trading Gold CFDs in a US Dollar market
Trading Gold CFDs in a US Dollar market requires specific strategies that consider the unique characteristics of gold and the market. Following are some specific strategies traders can use to effectively trade Gold CFDs in a US Dollar market.
Trade the Correlation Between Gold and the US Dollar: Gold and the US Dollar have an inverse relationship, meaning that when the value of the US Dollar rises, the price of gold falls, and vice versa. Traders can use the correlation to their advantage by monitoring the value of the US Dollar and trading Gold CFDs accordingly. For example, if the US Dollar is weakening, a trader may consider buying Gold CFDs, as the weakening US Dollar may lead to an increase in the price of gold.
Monitor Gold Supply and Demand: Gold prices can also be influenced by changes in supply and demand. Traders should stay informed about news and events that could impact the supply and demand of gold, such as mining strikes, changes in gold production, or changes in demand from critical consumers. Traders can apply and process the information to derive informed trading decisions.
Technical Analysis to explore vital price Levels: Technical analysis can be a powerful tool for trading Gold CFDs. Traders can systematically apply technical indicators such as moving averages (MAs), support and resistance levels, RSI, and trend lines to identify vital levels where the price of gold may experience a reversal or break out. For example, if a trader notices that the price of gold has been consistently bouncing off a particular support level, they may consider buying Gold CFDs at that level.
Seasonal patterns to time trades: Seasonal patterns can influence gold prices. For example, demand for gold tends to increase during the wedding season in India, which is one of the largest consumers of gold. Traders can apply the information to time their trades and take advantage of seasonal price movements.
Risk Management Strategies: Managing risk is crucial to any trading strategy, and trading Gold CFDs is no exception. Traders can implement stop-loss orders and position sizing to manage risk exposure. For instance, a trader may execute a stop-loss order to automatically close out a position if the price of gold falls below a certain level, thus limiting their potential losses.
How to hedge against currency risks when trading Gold CFDs
Trading Gold CFDs involves currency risks, as the price of gold is denominated in US Dollars while the trader's account may be denominated in a different currency. Currency risk arises when there is uncertainty about the future exchange rate between the trader's currency and the US Dollar. There are some effective strategies that traders can use to hedge against currency risks when trading Gold CFDs.
Use a Currency-Hedged Account: One of the most effective ways to hedge against currency risk when trading Gold CFDs is to use a currency-hedged account. In this type of account, the trader's account is denominated and operated in the same currency as the Gold CFDs they are trading. For example, if a trader is based in the Eurozone and is trading Gold CFDs denominated in US Dollars, they could open a Euro-denominated account. It would eliminate currency risk, as any gains or losses from the Gold CFDs would be denominated in euros.
Trade Gold CFDs in Local Currency: Another way to hedge against currency risk is to trade Gold CFDs denominated in local currency. Many brokers offer Gold CFDs denominated in multiple currencies, including major currencies such as Euros, British Pounds, and Japanese Yen. By trading Gold CFDs denominated in local currency, you eliminate currency risk, as any gains or losses from the Gold CFDs would be denominated in local currency.
Use Currency Options: Currency options can be applied to hedge against currency risk. A currency option gives the holder the exclusive right, but not any obligation, to trade a specific quantum of currency at a predetermined exchange rate. For example, a trader could purchase a call option on the US Dollar/Euro exchange rate to hedge against currency risk when trading Gold CFDs denominated in US Dollars. If the US Dollar depreciates against the Euro, the trader will exercise the option, denominating their profits in Euros.
Use Forward Contracts: forward contracts are another financial instrument that can be used to hedge against currency risk. A forward contract is a formal agreement/arrangement to trade a specific quantum of currency at a specified exchange rate at a future date. For example, a trader could enter into a forward contract to sell US Dollars and buy euros at a predetermined exchange rate to hedge against currency risk when trading Gold CFDs denominated in US Dollars.
The importance of following current events and trends in the foreign exchange market
The foreign exchange (forex) market is a complex and dynamic marketplace constantly influenced by global events and trends. As such, forex traders must stay up-to-date with the latest news and trends in the market. The importance of following current events and trends in the forex market, as well as providing examples of how they can impact currency prices.
Understanding the Market Fundamentals: Macroeconomic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and employment data heavily influence the forex market. Awareness of the latest developments in these areas can help traders to derive more logical and informed decisions about which currencies to trade. For example, if the US Federal Reserve raises interest rates, this is likely to increase the value of the US Dollar relative to other currencies.
Identifying Market Trends: Keeping abreast of current events can help traders identify emerging market trends. For instance, a rapid enhancement in demand for a particular currency may indicate a direction that can be capitalized on. On the other hand, increased political instability in a specific region could lead to decreased demand for local currency.
Responding to Market Volatility: Current events can also significantly impact market volatility. Events such as natural disasters, political turmoil, and unexpected economic data releases can cause sharp movements in currency prices. By staying informed about such events, traders can prepare for potential volatility and take steps to mitigate their risk. For example, a trader might reduce their position size or use stop-loss orders to limit their exposure to sudden price movements.
Identifying Trading Opportunities: Finally, keeping up with the latest news and trends in the forex market can help traders identify potential trading opportunities. For instance, if a country's economic data is more potent than expected, it could enhance demand for that country's currency. Similarly, if a country's central bank announces an expansionary monetary policy, it could decrease the value of its currency relative to others.
VI. Conclusion
Summary of the correlation between Gold CFDs and the US Dollar
Gold, a safe-haven asset, is what investors focus on buying during times of uncertainty or market turmoil. It is because gold has historically retained its value, even during economic downturns. As a result, gold prices are often inversely correlated with the US Dollar. When the US Dollar is weak, gold prices tend to rise, and when the US Dollar is robust, gold prices tend to fall.

The inverse correlation between Gold CFDs and the US Dollar can be attributed to key factors. Firstly, gold is priced in US Dollars, which means that changes in the US Dollar value directly impact the price of gold. When the US Dollar strengthens, it requires lesser US Dollars to buy the exact quantum of gold, which can lead to a decrease in gold prices. Conversely, when the US Dollar weakens, it takes more US Dollars to buy the same amount of gold, which can lead to an increase in gold prices.
Secondly, the US Dollar is often seen as a safe-haven currency, similar to gold. During economic adversities, investors tend to flock to the US Dollar, which can strengthen the currency. It, in turn, can lead to a decrease in the price of gold.
Advice for investors considering trading Gold CFDs in a US Dollar market
Trading Gold CFDs in a US Dollar market can be an exciting and potentially profitable venture, but it is also a complex and risky activity. Advice is provided for investors considering trading Gold CFDs in a US Dollar market, including focusing on risk management, market analysis, and trading strategies.
Develop a risk management strategy: One of the most important aspects of trading Gold CFDs is managing risk. It includes setting stop-loss orders to limit losses if the market moves against them and determining risk tolerance and position sizing. It is essential to have a well-defined risk management strategy before entering the market.
Stay updated with news and analysis: To make logical trading decisions, it is crucial to stay updated with the news and analysis regarding the gold market and the US Dollar. It involves monitoring economic indicators such as interest rates and inflation and tracking geopolitical developments that may impact the market.
Use Technical Analysis: Technical analysis involves using price charts and other indicators to identify trends and patterns in the market. It can help you make more informed trading decisions and identify potential entry and exit points. Various technical analysis tools are available, including MAs, RSI, trend lines, and chart patterns.
Consider correlations with other assets: Inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical risks often influence gold prices. Therefore, it is essential to consider how other assets, such as currencies and commodities, perform relative to gold. For example, if the US Dollar is weakening, it may be an ideal time to buy Gold CFDs as a hedge against currency risk.
Be prepared for volatility: The gold market can be highly volatile, with prices sometimes experiencing significant swings quickly. As such, it is vital to be prepared for volatility and have a trading strategy that accounts for potential market fluctuations.




