- Mexico's sugar production for 2023/24 reduced significantly due to widespread drought.
- Lower rainfall affecting cane growing regions, impacting yield forecasts.
- U.S. sugar supply shifts with decreased imports from Mexico and the Philippines.
- Louisiana expects increased cane and beet sugar production, altering the supply landscape.
As Mexico's sugar production faces a daunting setback due to widespread drought, global markets brace for turbulence. The relentless dry spell threatens vital cane growing regions, igniting concerns about sugar yields and supply stability. Amidst these challenges, shifts in U.S. import patterns and rising local production in Louisiana add intrigue to the complex and volatile world of sugar trading. Understanding the latest USDA data and its implications on Sugar Futures and Contracts for Difference (CFDs) requires a detailed analysis focusing on both U.S. and global perspectives.
Review of USDA Data
Mexico's Reduced Production: The reduction in Mexico's sugar production for the 2023/24 season by 245K metric tons is primarily due to widespread drought conditions affecting key growing areas, especially in the western Pacific region and San Luis Potosi. This reduction in production forecasts indicates potential challenges in meeting the expected output due to adverse weather conditions.
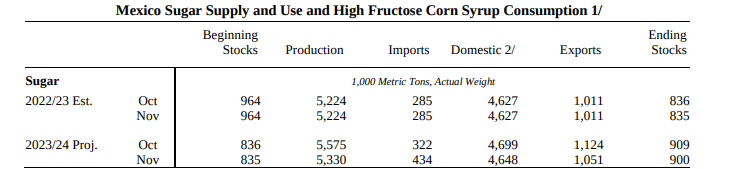
Source: USDA.gov
Rainfall Impact on Yields: The data highlights that rainfall in cane growing regions is approximately 23 percent below normal levels. This deficit in precipitation is comparable to the situation experienced in 2019, a year characterized by notably lower agricultural yields. Lower rainfall directly affects the yields, impacting the overall forecasted sugar production for the upcoming season.
Yield Projections: The USDA analysis projects a national sugar yield of 61.3 metric tons per hectare for the upcoming season. This projection is lower than the yield recorded in 2019 (62.9 MT/ha) but higher than the yield of the preceding year (59.0 MT/ha). It's important to note that various factors, including irrigation and fertilization practices, significantly influence yield forecasting, implying potential variability in actual yields.
Supply and Use Changes in Mexico: The reduced production in Mexico triggers adjustments in various components of supply and use. Decreased deliveries into the IMMEX program, lower production of low polarity sugar for export, adjusted ending stocks to meet delivery requirements, and increased imports as a residual are measures taken to counterbalance the reduced domestic production.
U.S. Sugar Supply Changes: The changes in the U.S. sugar supply for 2023/24 reflect a mix of factors. Decreased TRQ raw sugar imports from the Philippines due to the allocation of all production for domestic use, reduced imports from Mexico due to lower refined sugar slated for the U.S. market, and an increase in projected high-tier tariff imports contribute to altering the supply landscape.
Production Changes in Louisiana (Cane) and Beet Sugar: Louisiana's cane sugar production for 2023/24 is expected to increase by 48,947 STRV to 1.787 million mostly due to a higher sugarcane yield forecast by NASS. Additionally, beet sugar production is anticipated to increase by 211,290 STRV to 5.363 million based on higher sugarbeet yields, an increase in recovery, and adjustments for early season production.
Possible Implications on Prices of Sugar Futures and CFDs
Supply Shortfall and Price Volatility: The reduction in Mexico's sugar production due to adverse weather conditions may result in a supply shortfall, impacting the global sugar market. A reduced supply against stable or increasing demand often leads to upward pressure on prices. Market volatility is expected due to uncertainties surrounding the actual impact of the reduced production on the market equilibrium.
Market Reaction to Weather-Related Factors: Historically, weather-related disruptions, especially drought conditions affecting key producing regions, have resulted in heightened market sensitivity. Uncertainty regarding the actual yield losses and the ability of other producing regions to compensate for the deficit might result in speculative activities and consequent price fluctuations in Sugar Futures and CFDs.
U.S. Market Dynamics: Changes in the U.S. sugar market, including alterations in import quantities and increased domestic production in Louisiana, could influence global sugar prices. Import reductions from Mexico and the Philippines, coupled with increased high-tier tariff imports, might impact the balance of supply and demand, potentially affecting price directions.
Global Supply-Demand Balance: The reduced production in Mexico could disrupt the balance between sugar demand and supply in the global market. If other major producers do not compensate for the deficit adequately, it might lead to a tighter supply scenario, resulting in increased prices, especially if demand remains robust or increases.
Weather Dependency and Future Forecasts: The potential impact of weather conditions remains a critical factor in determining future sugar prices. Any improvement or worsening of drought conditions in Mexico and other significant producing regions could significantly alter production forecasts and subsequent market reactions.
Sugar Price Technical Take
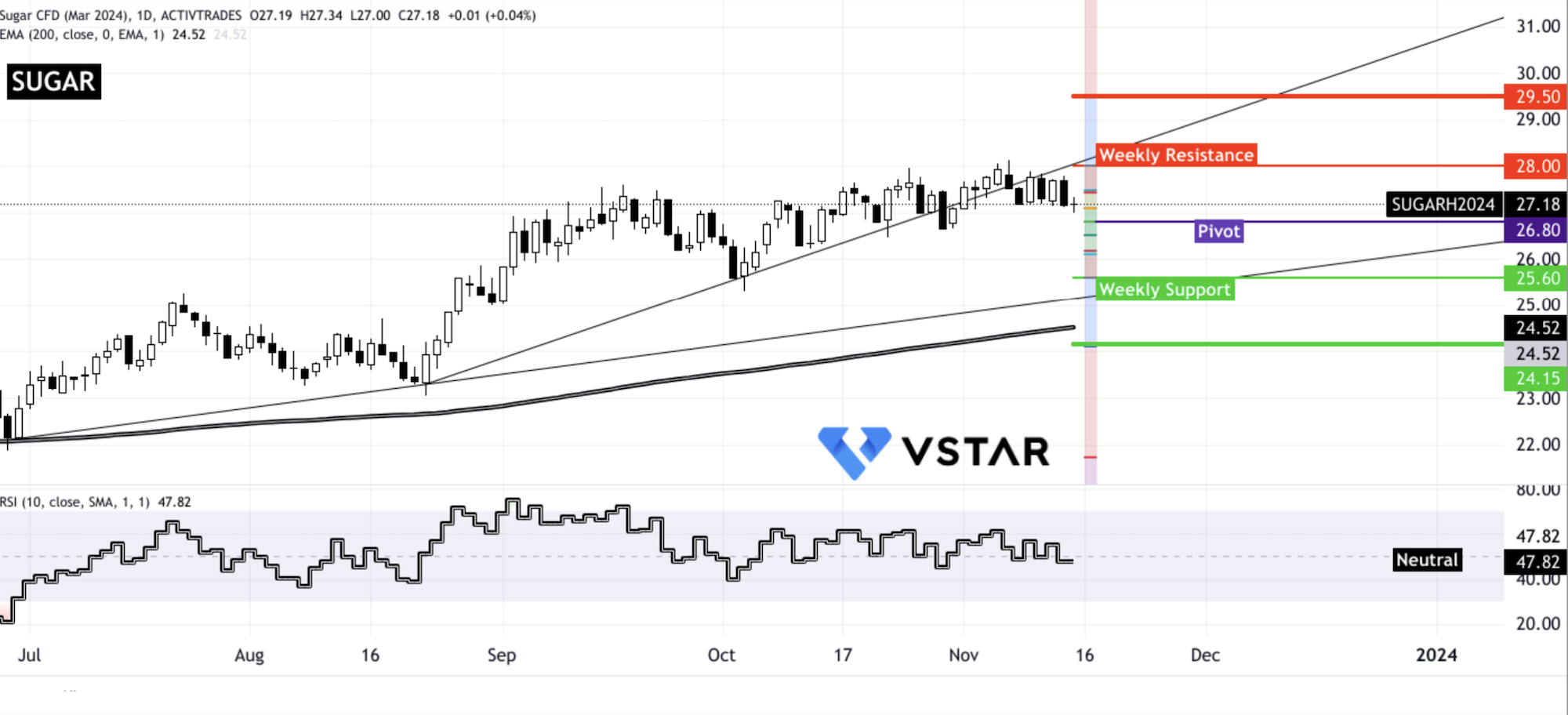
Sugar CFDs and Futures have shown a consistent uptrend, finding elevating support at the 200-day Exponential Moving Average (EMA). This upward momentum has gained short-term acceleration since August 2023. Despite this, the Relative Strength Index (RSI) indicates temporary neutral momentum from October 2023. Technical analysis suggest that the prices may experience potential resistance levels at $29.50 and $28.00 in the upcoming weeks, while support levels have emerged at $25.60 and $24.15 on the downside.
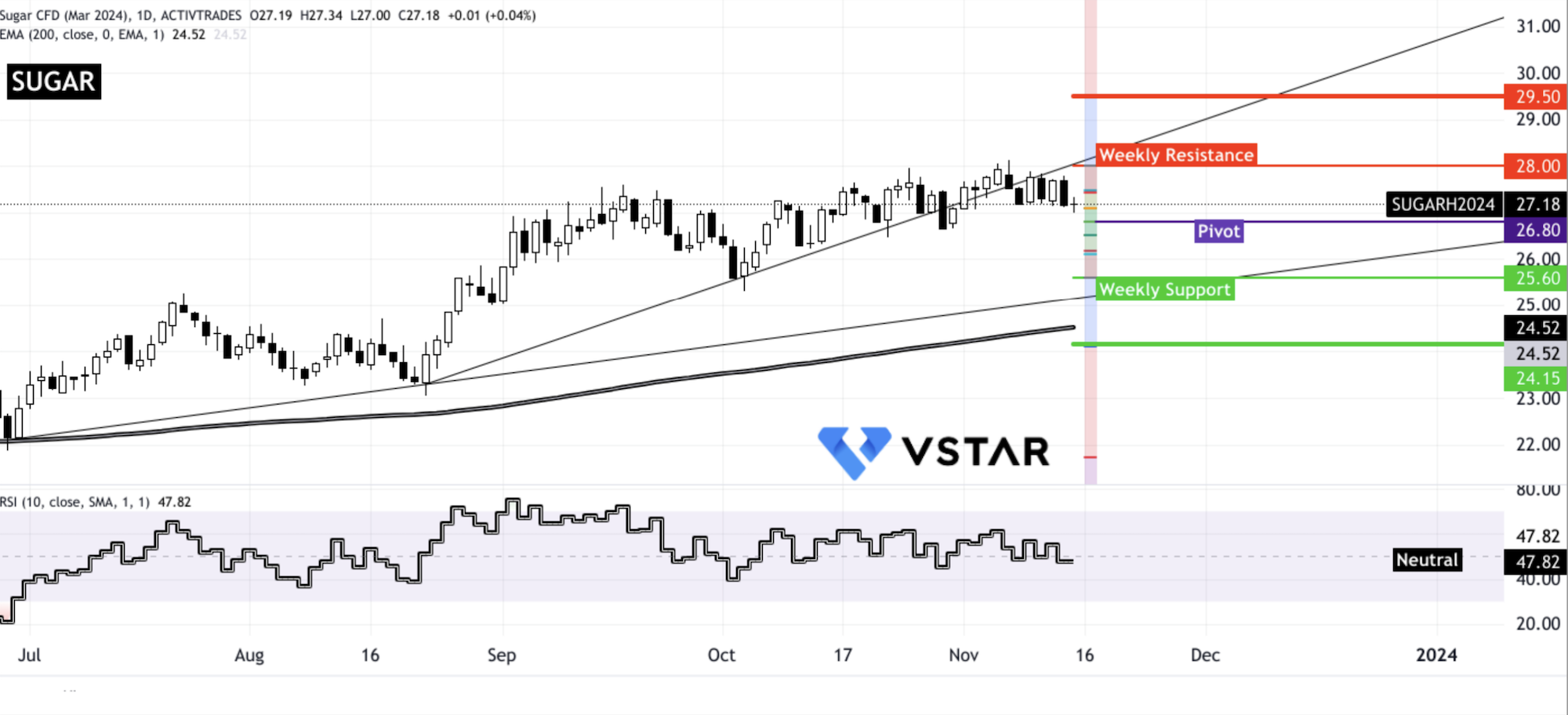
Source: tradingview.com
In summary, the USDA data suggests potential challenges in sugar production due to adverse weather conditions in Mexico, indicating a likelihood of supply constraints. The interplay between supply adjustments, weather patterns, and changes in the U.S. market dynamics will likely influence the direction of Sugar Futures and CFDs prices. The possibility of supply shortages amidst stable or growing demand might lead to increased market volatility and upward price pressures in Sugar Futures and CFDs if production deficits persist.