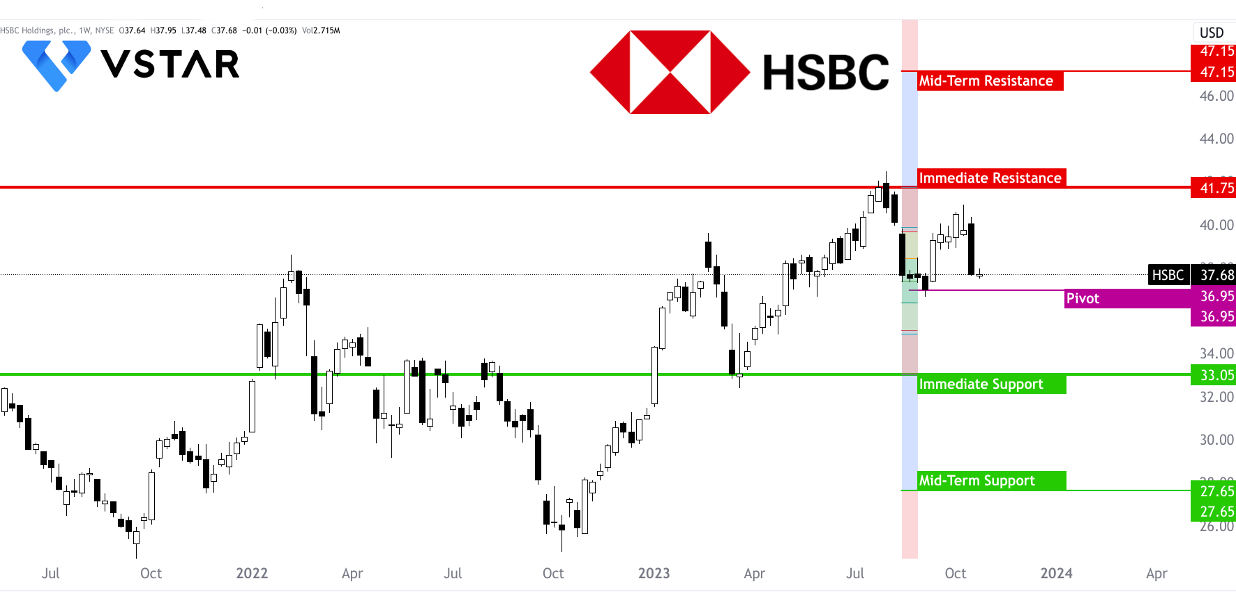
HSBC (HKG:0005) is a global banking giant with a rich history dating back to the 19th century. Over the years, the bank has developed several fundamental strengths that underpin its potential for rapid growth. These strengths, backed by a stable strategy, robust financial performance, and a focus on diversification, make HSBC a formidable player in the banking industry.
Stable and Proven Strategy (Strategy Stability)
HSBC's strength begins with its stable and proven strategy. The bank's strategic framework has remained consistent, providing a solid foundation for growth. This strategy is succinctly summarized by four key pillars, which have remained unchanged. The stability in strategy allows HSBC to focus on executing its plan without constant shifts in direction, providing clarity to both internal and external stakeholders. This stability instills confidence and trust in the bank's ability to deliver on its strategic objectives.
Strong Financial Performance (Profitability)
A critical indicator of HSBC's strength is its strong financial performance. In H1 2023, the bank reported impressive financial results. This included broad-based profits and revenue growth across its global businesses and geographies. The hallmark of a strong financial institution is its ability to generate profits consistently, and HSBC has demonstrated this ability in the form of robust financial figures.
One key measure of financial performance is the annualized return on tangible equity, which reached 22.4% as of H1 2023. This is a remarkable achievement, signifying the bank's capability to deliver strong returns to its shareholders. In a competitive banking landscape, generating such high returns is a testament to HSBC's efficiency and effectiveness in managing its assets and operations.
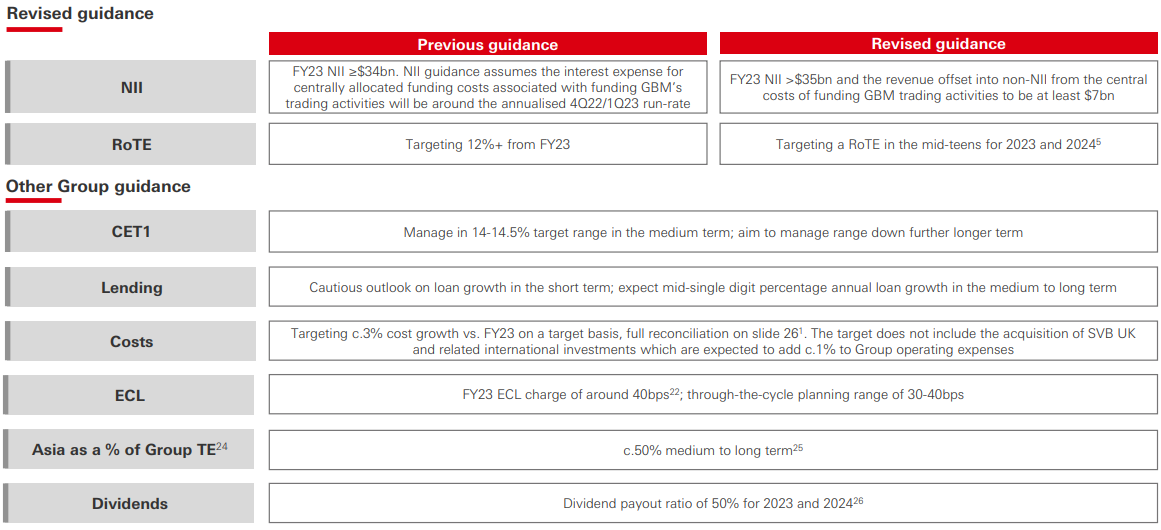
Source: H1 2023 results
Capital Generation (Capital Adequacy)
Another critical strength that supports HSBC's rapid growth potential is its ability to generate capital. In the banking industry, capital is the lifeblood that fuels expansion, investments, and the pursuit of new opportunities. HSBC's capacity to generate and maintain strong capital levels is a strategic advantage.
The bank's strong capital generation allows it to fund various initiatives, including international expansion, technology investments, and risk management. Capital adequacy is not just a regulatory requirement but also a strategic lever that enables HSBC to seize growth opportunities, weather economic downturns, and ensure the long-term sustainability of the business.
Diversified Revenue Streams (Revenue Diversification)
HSBC's focus on diversifying its revenue streams is a vital strength for rapid growth. Over-reliance on any single revenue source can expose a bank to significant risks. Therefore, the bank's focus on expanding its sources of income helps mitigate this risk and contributes to its long-term stability.
A tangible demonstration of this strength is seen in the strong revenue growth within specific business segments. For instance, the Transaction Banking segment witnessed a remarkable 63% increase in revenue. Diversification in revenue sources, including foreign exchange and global payment solutions, showcases the bank's adaptability to changing market dynamics and its ability to capture revenue opportunities across diverse areas of its operations.
International Connectivity (Global Expansion)
HSBC's international connectivity is a pivotal strength that supports its growth strategy. International expansion opens up new markets, clients, and revenue opportunities. The bank has successfully grown its wholesale cross-border client business in the first half by approximately 50%. This expansion was observed in various regions, driven by higher interest rates.
In addition to its global business expansion, HSBC's international proposition in Wealth and Personal Banking continues to gain traction. The number of international WPB (Wealth and Personal Banking) customers has increased by 8% over the last 12 months, reaching 6.3 million. Importantly, these international customers generate around 2.5 times the average customer revenue, underscoring the financial benefit of international connectivity.
Business Transformation and Asset Reallocation (Strategic Focus)
HSBC's strategic focus on business transformation and asset reallocation is a powerful driver of its rapid growth potential. The ability to adapt and respond to market conditions by reallocating capital from less strategic or low-connectivity businesses into higher-growth international opportunities is a testament to the bank's agility and strategic acumen.
For example, the sale of banking operations in Canada is planned for early 2024, with a special dividend of $0.21 per share afterward. These divestitures, along with the disposal of non-core assets such as the Greek business, Russian operations, and changes in business operations in Oman and New Zealand, demonstrate HSBC's commitment to realigning its portfolio for optimal growth.
Wealth Business Expansion (Wealth Management Growth)
HSBC's focus on expanding its wealth and insurance business is a clear strength. The company's digitally enabled wealth and insurance business in Mainland China, boasting 1,400 wealth planners, has been driving significant new business growth. Furthermore, HSBC's entry into markets like India with Global Private Banking and the launch of HSBC Innovation Banking emphasize its pursuit of growth opportunities in emerging markets and industries.
The growth potential in wealth management and insurance is significant, and HSBC's strategic investments in this area position it to capitalize on the increasing demand for these financial services in the Asia-Pacific region and beyond.
Diversification of Fee Income (Fee Income Growth)
HSBC's focus on diversifying revenue by growing fee income is a fundamental strength that enhances its growth potential. Fee income is an essential component of the bank's revenue mix, and its growth contributes to financial stability. For example, fee income in Commercial Banking saw a notable 6% increase in the first half.
Collaboration revenues between HSBC's global businesses have also grown by 5%. This is particularly significant in a relatively low-growth economic environment because it allows the bank to drive growth from within the organization, leveraging synergies and cross-selling opportunities.
Cost Discipline (Operational Efficiency)
HSBC's tight cost discipline is a crucial strength that complements its growth strategy. Cost management is a foundational principle in banking, and the bank's commitment to disciplined cost control is evident. The focus on cost savings and the allocation of resources to increase investment in digitization are key components of this strength.
For instance, the bank increased spending on technology by 12.8% in H1 2023, with technology expenses accounting for 23% of its target base operating expenses. This investment translates into faster services, reduced friction in customer interactions, and more competitive products. Such operational efficiency improvements not only enhance the customer experience but also contribute to cost savings in the long run.
Sustainable Finance and ESG Focus (Sustainability Commitment)
HSBC's commitment to sustainable finance and its role as an enabler of the net-zero transition are strengths that align with the growing demand for Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG)-focused investments. The bank's provision and facilitation of $45 billion in sustainable finance and investments in the first half demonstrate its active participation in this growing segment.
Sustainable finance includes capital markets financing and on-balance-sheet lending to clients. HSBC's focus on sustainability has led to recognition, such as being named "Best Bank for Sustainable Finance in Asia" by Euromoney for the sixth consecutive year. This commitment not only aligns with ESG principles but also positions HSBC as a responsible financial institution, attracting clients who prioritize sustainable investments.
Distribution of Capital to Shareholders (Capital Returns)
HSBC's plan to return capital to shareholders through dividends and share buybacks is another strength. It provides a clear path for rewarding investors who have supported the bank. These capital returns indicate a commitment to shareholders and an acknowledgment of the importance of delivering value to those who have invested in the bank.
Capital returns also signify a robust balance sheet and the ability to generate surplus capital, which can be channeled back to investors or utilized for strategic investments, further contributing to growth potential.
Stable Credit Quality (Risk Management)
Maintaining a stable credit quality is fundamental to the long-term growth and sustainability of a bank. HSBC's ability to preserve credit quality in the face of headwinds and challenges is a notable strength. It has managed to keep the expected credit losses charge at normalized levels.
Stable credit quality is essential for maintaining investor and depositor confidence, as well as supporting lending activities. A bank's credit quality serves as a barometer of its risk management capabilities, and HSBC's consistency in this area is a strength that underpins its growth potential.
Specific Risks
- HSBC operates in various regions and lends to a diverse customer base, making it susceptible to credit risk due to economic fluctuations and borrower creditworthiness.
- HSBC's global presence means it is vulnerable to fluctuations in various financial markets, which can impact the value of its assets and liabilities.
- HSBC operates in regions with diverse geopolitical and country-specific risks. Political instability, trade tensions, sanctions, or changes in government policies can impact the bank's operations in different countries.
- Economic challenges (like a potential recession) in key markets can affect HSBC's lending activities, customer demand, and asset quality.
- A significant and unexpected shift in interest rates can impact HSBC's profitability.
In conclusion, HSBC's rapid growth potential is supported by a multifaceted array of strengths. These strengths include a stable and proven strategy, strong financial performance, capital generation capabilities, diversified revenue streams, international connectivity, strategic business transformation, wealth business expansion, fee income diversification, cost discipline, sustainability focus, capital distribution to shareholders, and stable credit quality.
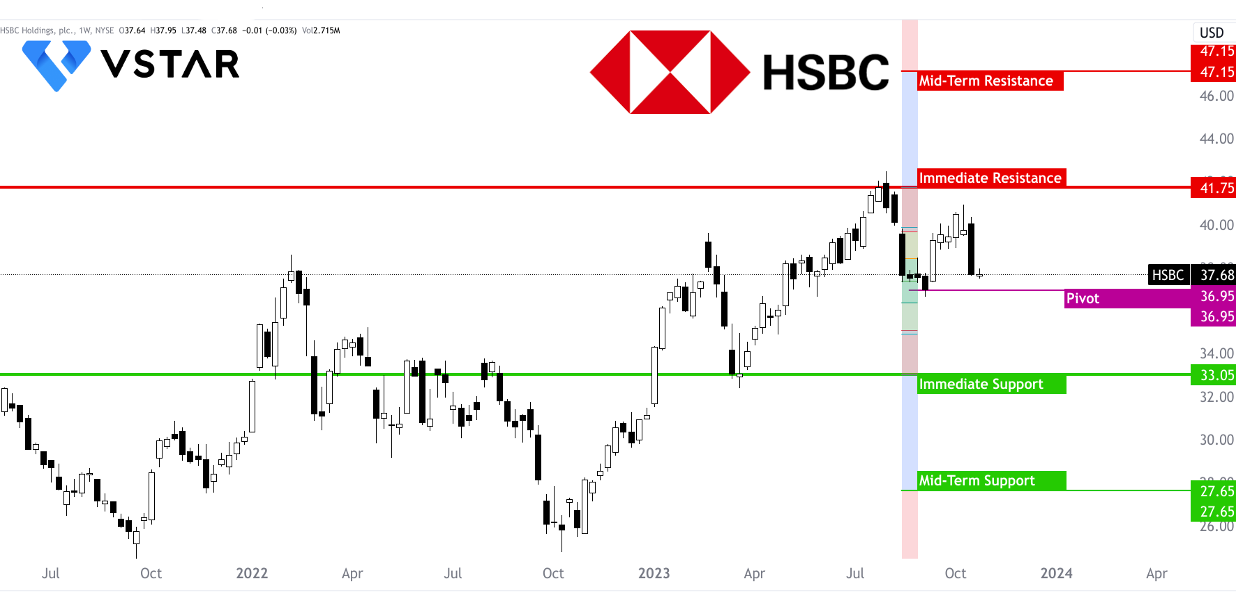
Source: tradingview.com