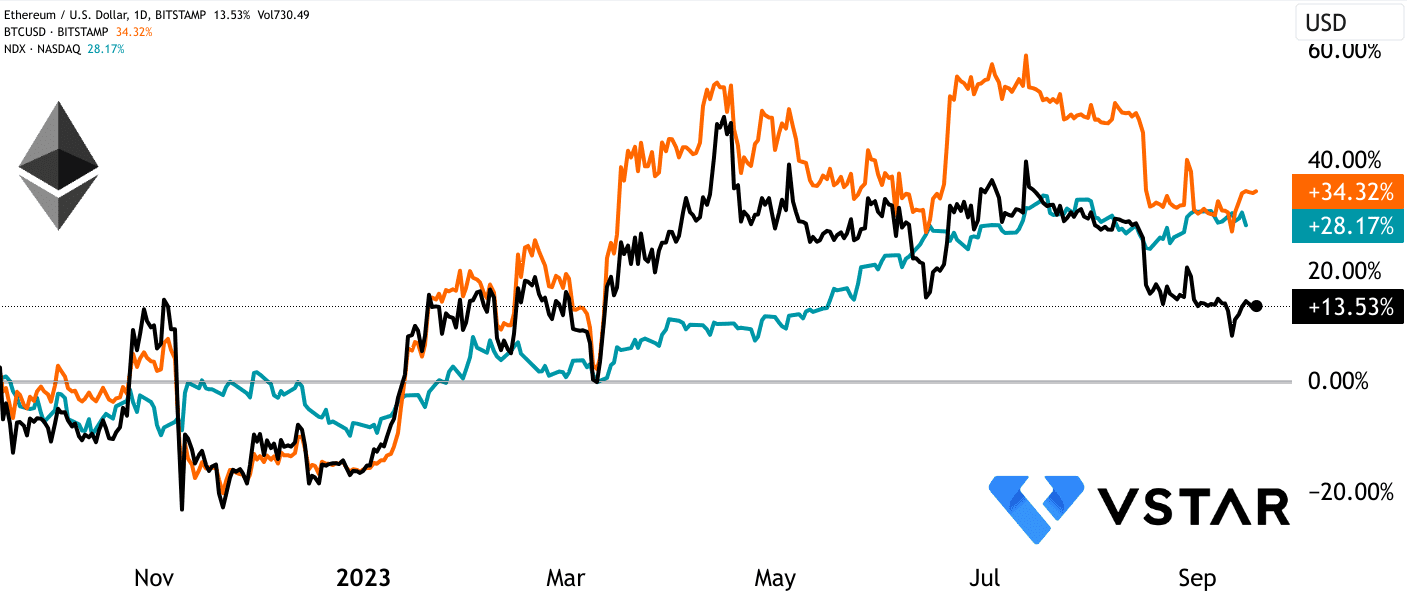
ETH’s underperformed as compared to other asset classes even a year after the Merge
The Ethereum ecosystem has undergone significant changes and challenges in the year following the implementation of the Merge, transitioning from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This transition has had multifaceted implications for Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network. Let's delve into a critical, forward-looking analysis of these implications.
Impact of the Ethereum Merge on ETH's supply dynamics
First and foremost, the Ethereum Merge has had a profound impact on ETH's supply dynamics. Since the Merge, there has been a net supply reduction of nearly 300K ETH (-0.25%). This shift to PoS not only curtails the rate of new ETH entering circulation but also actively removes ETH from supply through burning mechanisms. As a result, ETH has transformed into a deflationary currency, which could potentially boost its scarcity value in the long term.
One of the most significant consequences of this transition is the reduction in mining supply. PoS eliminates the need for miners, who previously played a central role in validating transactions through computational work. This has had two notable effects. First, it has reduced the selling pressure from miners, as they no longer need to liquidate mined ETH to cover operational costs. Second, it has fundamentally changed the incentives for network participants. Validators in PoS must hold a minimum amount of ETH, effectively locking up their assets, and are rewarded with transaction fees and issuance. This change may lead to increased price stability, as validators are less likely to engage in short-term speculation.
Environmental concerns have also played a pivotal role in Ethereum's transition. PoS is significantly more energy-efficient compared to PoW, aligning with global sustainability trends. This transition can potentially attract more ethically conscious investors and institutions that are looking for blockchain networks with reduced carbon footprints.
ETH's market valuation has not seen substantial growth
However, despite these positive changes, ETH's market valuation has not seen substantial growth since the Merge, in stark contrast to Bitcoin and NASDAQ-100, which have surged by nearly 34% and 28% over the 12 months. The stagnant price may be attributed to factors like concerns over gas fees. Ethereum's transition has not significantly alleviated the gas fee problem, which can deter users and developers from the network due to high transaction costs. This issue has been identified as a critical challenge, and Ethereum Improvement Proposal (EIP)-4844, also known as "proto-danksharding," is positioned as a potential solution.
EIP-4844 aims to reduce gas fees and enhance transaction throughput by introducing data blobs that efficiently process data without permanent storage on the Ethereum virtual machine. If successful, this upgrade could address a major pain point, making Ethereum more accessible and attractive for users and developers. The outcome of EIP-4844 is crucial for ETH's future, as it has the potential to revitalize interest in the Ethereum ecosystem and positively impact ETH's market performance.
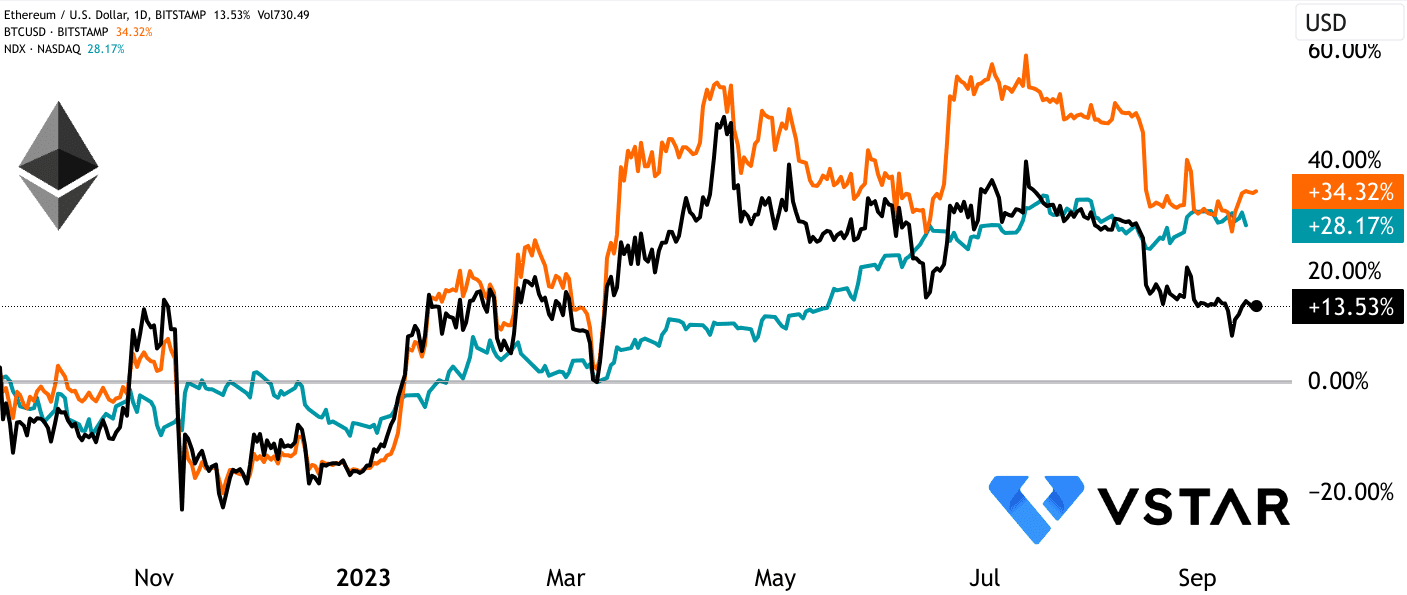
Data source: tradingview.com